Probing the 3D architecture of the plant nucleus with microscopy approaches: challenges and solutions
- PMID: 31362571
- PMCID: PMC6682351
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2019.1644592
Probing the 3D architecture of the plant nucleus with microscopy approaches: challenges and solutions
Erratum in
-
Correction.Nucleus. 2020 Dec;11(1):i. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2019.1669933. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Nucleus. 2020. PMID: 31532711 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
The eukaryotic cell nucleus is a central organelle whose architecture determines genome function at multiple levels. Deciphering nuclear organizing principles influencing cellular responses and identity is a timely challenge. Despite many similarities between plant and animal nuclei, plant nuclei present intriguing specificities. Complementary to molecular and biochemical approaches, 3D microscopy is indispensable for resolving nuclear architecture. However, novel solutions are required for capturing cell-specific, sub-nuclear and dynamic processes. We provide a pointer for utilising high-to-super-resolution microscopy and image processing to probe plant nuclear architecture in 3D at the best possible spatial and temporal resolution and at quantitative and cell-specific levels. High-end imaging and image-processing solutions allow the community now to transcend conventional practices and benefit from continuously improving approaches. These promise to deliver a comprehensive, 3D view of plant nuclear architecture and to capture spatial dynamics of the nuclear compartment in relation to cellular states and responses. Abbreviations: 3D and 4D: Three and Four dimensional; AI: Artificial Intelligence; ant: antipodal nuclei (ant); CLSM: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy; CTs: Chromosome Territories; DL: Deep Learning; DLIm: Dynamic Live Imaging; ecn: egg nucleus; FACS: Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting; FISH: Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization; FP: Fluorescent Proteins (GFP, RFP, CFP, YFP, mCherry); FRAP: Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching; GPU: Graphics Processing Unit; KEEs: KNOT Engaged Elements; INTACT: Isolation of Nuclei TAgged in specific Cell Types; LADs: Lamin-Associated Domains; ML: Machine Learning; NA: Numerical Aperture; NADs: Nucleolar Associated Domains; PALM: Photo-Activated Localization Microscopy; Pixel: Picture element; pn: polar nuclei; PSF: Point Spread Function; RHF: Relative Heterochromatin Fraction; SIM: Structured Illumination Microscopy; SLIm: Static Live Imaging; SMC: Spore Mother Cell; SNR: Signal to Noise Ratio; SRM: Super-Resolution Microscopy; STED: STimulated Emission Depletion; STORM: STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy; syn: synergid nuclei; TADs: Topologically Associating Domains; Voxel: Volumetric pixel.
Keywords: Three-dimensional microscopy imaging; image processing and analysis; live imaging; nuclear organization; plant nucleus; tracking; whole-mount.
Figures
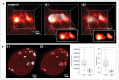
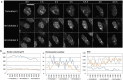
References
-
- Meier I. LINCing the eukaryotic tree of life - towards a broad evolutionary comparison of nucleocytoplasmic bridging complexes. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(19):3523–3531. - PubMed
-
- van Driel R, Fransz P. Nuclear architecture and genome functioning in plants and animals: what can we learn from both? Exp Cell Res. 2004;296(1):86–90. - PubMed
-
- Sotelo-Silveira M, Chavez Montes RA, Sotelo-Silveira JR, et al. Entering the next dimension: plant genomes in 3D. Trends Plant Sci. 2018;23(7):598–612. - PubMed
-
- Grob S, Grossniklaus U. Chromosome conformation capture-based studies reveal novel features of plant nuclear architecture. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017;36:149–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
