A Novel Approach of Drug Localization through Development of Polymeric Micellar System Containing Azelastine HCl for Ocular Delivery
- PMID: 31362666
- PMCID: PMC7040519
- DOI: 10.2174/2211738507666190726162000
A Novel Approach of Drug Localization through Development of Polymeric Micellar System Containing Azelastine HCl for Ocular Delivery
Abstract
Background: Development of polymeric micelles for the management of allergic conjunctivitis to overcome the limitations of topical installation, such as poor patient compliance, poor stromal permeability, and significant adverse effects, increase precorneal residence time and efficacy, and also control the release of drug at the target site.
Objective: The investigation was aimed at developing a polymeric micellar system of Azelastine HCl for Ocular Delivery.
Methods: Drug loaded micelles of tri-block copolymers Pf 127 were prepared by Thin Film hydration method. The polymeric micelles formulations (F1 to F9) were assessed for entrapment efficiency, micelle size, in vitro permeation, ex vivo transcorneal permeation, in vivo Ocular Irritation, and Histology.
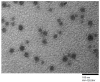
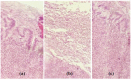
Results: Optimized micelles formulation (F3), with the lowest micelle size of 92 nm, least polydispersity value of 0.135, highest entrapment efficiency of 95.30 ± 0.17%, and a cumulative drug permeation of 84.12 ± 1.26% in 8h, was selected to develop pH-sensitive micelles loaded carbopol in situ gel. The optimized in situ gel (G4) proved to be superior in its ex vivo transcorneal permeation when compared with Market Preparation and pure drug suspension, exhibiting 43.35 ± 1.48% Permeation with zero-order kinetics (r2 = 0.9944) across goat cornea. Transmission Electron microscopy revealed spherical polymeric micelles trapped in the gel matrix. A series of experiments showed hydration capability, non-irritancy, and histologically safe gel formulation that had appropriate handling characteristics.
Conclusion: A controlled release pH-sensitive ocular formulation capable of carrying the drug to the anterior section of the eye via topical delivery was successfully developed for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.
Keywords: Azelastine HCl; entrapment efficiency; ex vivo transcorneal permeation; histology; in vitro permeation; in vivo ocular irritation; transmission electron microscopy; tri-block copolymers..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures




References
-
- Kuno N., Fujii S. Recent advances in ocular drug delivery systems. Polymers (Basel) 2011;3(1):193–221.
-
- Danion A., Arsenault I., Vermette P. Antibacterial activity of contact lenses bearing surface-immobilized layers of intact liposomes loaded with levofloxacin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007;96(9):2350–2363. - PubMed
-
- Short B.G. Safety evaluation of ocular drug delivery formulations: techniques and practical considerations. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008;36(1):49–62. - PubMed
-
- Gulsen D., Chauhan A. Ophthalmic drug delivery through contact lenses. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004;45(7):2342–2347. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

