IRESpy: an XGBoost model for prediction of internal ribosome entry sites
- PMID: 31362694
- PMCID: PMC6664791
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-2999-7
IRESpy: an XGBoost model for prediction of internal ribosome entry sites
Abstract
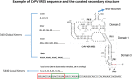
Background: Internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) are segments of mRNA found in untranslated regions that can recruit the ribosome and initiate translation independently of the 5' cap-dependent translation initiation mechanism. IRES usually function when 5' cap-dependent translation initiation has been blocked or repressed. They have been widely found to play important roles in viral infections and cellular processes. However, a limited number of confirmed IRES have been reported due to the requirement for highly labor intensive, slow, and low efficiency laboratory experiments. Bioinformatics tools have been developed, but there is no reliable online tool.
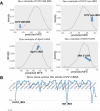
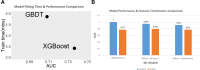
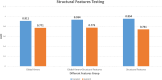
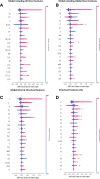
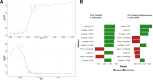
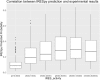
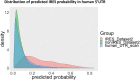
Results: This paper systematically examines the features that can distinguish IRES from non-IRES sequences. Sequence features such as kmer words, structural features such as QMFE, and sequence/structure hybrid features are evaluated as possible discriminators. They are incorporated into an IRES classifier based on XGBoost. The XGBoost model performs better than previous classifiers, with higher accuracy and much shorter computational time. The number of features in the model has been greatly reduced, compared to previous predictors, by including global kmer and structural features. The contributions of model features are well explained by LIME and SHapley Additive exPlanations. The trained XGBoost model has been implemented as a bioinformatics tool for IRES prediction, IRESpy (https://irespy.shinyapps.io/IRESpy/), which has been applied to scan the human 5' UTR and find novel IRES segments.
Conclusions: IRESpy is a fast, reliable, high-throughput IRES online prediction tool. It provides a publicly available tool for all IRES researchers, and can be used in other genomics applications such as gene annotation and analysis of differential gene expression.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Internal ribosome entry site (IRES); Machine learning; XGBoost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DeepIRES: a hybrid deep learning model for accurate identification of internal ribosome entry sites in cellular and viral mRNAs.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jul 25;25(5):bbae439. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae439. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39234953 Free PMC article.
-
IRESPred: Web Server for Prediction of Cellular and Viral Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES).Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 6;6:27436. doi: 10.1038/srep27436. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27264539 Free PMC article.
-
IRES-dependent translated genes in fungi: computational prediction, phylogenetic conservation and functional association.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 15;16:1059. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2266-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26666532 Free PMC article.
-
Searching for IRES.RNA. 2006 Oct;12(10):1755-85. doi: 10.1261/rna.157806. Epub 2006 Sep 6. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16957278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosomal Chamber Music: Toward an Understanding of IRES Mechanisms.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Aug;42(8):655-668. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28684008 Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA-encoded micropeptides: functions, mechanisms and implications.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Oct 23;10(1):450. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02175-0. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39443468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of machine learning model for diagnostic disease prediction based on laboratory tests.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 7;11(1):7567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87171-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33828178 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Binding Proteins as Regulators of Internal Initiation of Viral mRNA Translation.Viruses. 2022 Jan 19;14(2):188. doi: 10.3390/v14020188. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting COVID-19 disease severity from SARS-CoV-2 spike protein sequence by mixed effects machine learning.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Oct;149:105969. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105969. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36041271 Free PMC article.
-
Parvovirus B19 and Human Parvovirus 4 Encode Similar Proteins in a Reading Frame Overlapping the VP1 Capsid Gene.Viruses. 2024 Jan 26;16(2):191. doi: 10.3390/v16020191. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38399966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen T, Guestrin C. Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. 2016. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

