PLC-gamma-1 phosphorylation status is prognostic of metastatic risk in patients with early-stage Luminal-A and -B breast cancer subtypes
- PMID: 31362705
- PMCID: PMC6668079
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5949-x
PLC-gamma-1 phosphorylation status is prognostic of metastatic risk in patients with early-stage Luminal-A and -B breast cancer subtypes
Abstract
Background: Phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) is highly expressed in human tumours. Our previous studies reported that both stable and inducible PLCγ1 down-regulation can inhibit formation of breast-cancer-derived experimental lung metastasis. Further, high expression of PLCγ1 and its constitutively activated forms (i.e., PLCγ1-pY1253, PLCγ1-pY783) is associated with worse clinical outcome in terms of incidence of distant metastases, but not of local relapse in T1-T2, N0 breast cancer patients.
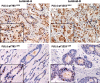
Methods: In the present retrospective study, we analysed the prognostic role of PLCγ1 in early breast cancer patients stratified according to the St. Gallen criteria and to their menopausal status. PLCγ1-pY1253 and PLCγ1-pY783 protein expression levels were determined by immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays, and were correlated with patients' clinical data, using univariate and multivariate statistical analyses.
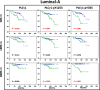
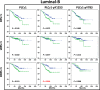
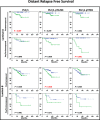
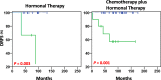
Results: In our series, the prognostic value of PLCγ1 overexpression was restricted to Luminal type tumours. From multivariate analyses, pY1253-PLCγ1High was an independent prognostic factor only in postmenopausal patients with Luminal-B tumours (hazard ratio [HR], 2.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1-5.3; P = 0.034). Conversely, PLCγ1-pY783High was a remarkably strong risk factor (HR, 20.1; 95% CI, 2.2-178.4; P = 0.003) for pre/perimenopausal patients with Luminal-A tumours.
Conclusions: PLCγ1 overexpression is a strong predictive surrogate marker of development of metastases in early Luminal-A and -B breast cancer patients, being able to discriminate patients with high and low risk of metastases. Therefore, targeting the PLCγ1 pathway can be considered of potential benefit for prevention of metastatic disease.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Luminal subtypes; Menopausal status; Phospholipase Cγ1; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

