Implementation of flipped classroom combined with problem-based learning: an approach to promote learning about hyperthyroidism in the endocrinology internship
- PMID: 31362729
- PMCID: PMC6668058
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-019-1714-8
Implementation of flipped classroom combined with problem-based learning: an approach to promote learning about hyperthyroidism in the endocrinology internship
Abstract
Background: With the development of medicine, new teaching methods, such as flipped classroom and problem-based learning (PBL), have received much attention in medical education. However, the implementation of flipped classroom combined with PBL in endocrinology education has not been well investigated. Considering that both two teaching methods may complement each other, therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate students' learning effectiveness acceptability of the pedagogy between traditional lecture-based teaching methods and the combination of flipped classrooms with PBL teaching methods in the endocrinology internship.
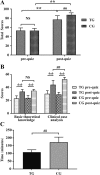
Methods: 74 fourth-year medical students at the Bengbu Medical College were enrolled in the endocrinology internship. Hyperthyroidism was chosen for the content of this study. The participants were randomly allocated into either the combination group of flipped classroom with PBL (CG) or the traditional lecture-based classroom group (TG). Both a pre-quiz and a post-quiz were conducted before and after the classes, respectively. All questions in the quizzes were classified into two aspects, basic theoretical knowledge and clinical case analyses based on the Bloom's Taxonomy. The scores were compared and students were required to complete the questionnaire to evaluate their perceptions and experience.
Results: The mean post-quiz scores of both the TG and the CG were higher than those of the pre-quiz. Additionally, the post-quiz showed that students in the CG had significantly higher scores in the TG. Further analysis found that after class, only the difference in clinical case analysis between CG and TG was significant. The scores of all items in the questionnaires were higher in the CG than in the TG. More students agreed that the combined teaching method could help to improve their performance, at the same time, it could increase their workload.
Conclusions: The combination of the flipped classroom and PBL teaching approach could be a better option over the traditional lecture-based classroom in the teaching of hyperthyroidism during endocrinology internship, although it can increase students' workload. To be widely accepted and implemented, further optimizations are required.
Keywords: Endocrinology; Flipped classroom; Hyperthyroidism; Internship; Problem-based learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Deshpande AN, Naik KS, Poonacha KS, Dave BH, Joshi NH, Mehta DH. Comparison of case-based learning and traditional learning style in final year BDS (bachelor of dental surgery) students in paediatric dentistry unit lesson. Applied Med Res. 2019;6(1):9–15. doi: 10.5455/amr.20180406075050. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

