Local ice cryotherapy decreases synovial interleukin 6, interleukin 1β, vascular endothelial growth factor, prostaglandin-E2, and nuclear factor kappa B p65 in human knee arthritis: a controlled study
- PMID: 31362785
- PMCID: PMC6668066
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1965-0
Local ice cryotherapy decreases synovial interleukin 6, interleukin 1β, vascular endothelial growth factor, prostaglandin-E2, and nuclear factor kappa B p65 in human knee arthritis: a controlled study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the anti-inflammatory effects of local cryotherapy in human non-septic knee arthritis.
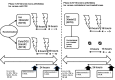
Methods: In the phase I of the study, patients were randomized to receive either ice (30 min; N = 16) or cold CO2 (2 min; N = 16) applied twice during 1 day at an 8-h interval on the arthritic knee. In phase II, 16 other ice-treated arthritic knees according to the same protocol were compared to the contralateral non-treated arthritic knees (N = 16). The synovial fluid was analyzed just before the first cold application, then 24 h later. IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-17A, VEGF, NF-kB-p65 protein, and PG-E2 levels were measured in the synovial fluid and compared before/after the two cold applications.
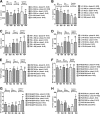
Results: Forty-seven patients were included (17 gouts, 11 calcium pyrophosphate deposition diseases, 13 rheumatoid arthritides, 6 spondyloarthritides). Local ice cryotherapy significantly reduced the IL-6, IL-1β, VEGF, NF-kB-p65, and PG-E2 synovial levels, especially in the microcrystal-induced arthritis subgroup, while only phosphorylated NF-kB-p65 significantly decreased in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis patients. Cold CO2 only reduced the synovial VEGF levels. In the phase II of the study, the synovial PG-E2 was significantly reduced in ice-treated knees, while it significantly increased in the corresponding contralateral non-treated arthritic knees, with a significant inter-class effect size (mean difference - 1329 [- 2232; - 426] pg/mL; N = 12).
Conclusions: These results suggest that local ice cryotherapy reduces IL-6, IL-1β, and VEGF synovial protein levels, mainly in microcrystal-induced arthritis, and potentially through NF-kB and PG-E2-dependent mechanisms.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03850392-registered February 20, 2019-retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Cytokines; Knee arthritis; Local cryotherapy; NF-kB; PG-E2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Welch V, Brosseau L, Shea B, McGowan J, Wells G, Tugwell P. Thermotherapy for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002826. - PubMed
-
- Cholewka A, Stanek A, Wójcik M, Sieroń-Stołtny K, Drzazga Z. Does local cryotherapy improve thermal diagnosis similar to whole-body cryotherapy in spinal diseases? J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:1155–1162. doi: 10.1007/s10973-016-5453-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

