A soluble tau fragment generated by caspase-2 is associated with dementia in Lewy body disease
- PMID: 31362787
- PMCID: PMC6668119
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-019-0765-8
A soluble tau fragment generated by caspase-2 is associated with dementia in Lewy body disease
Abstract
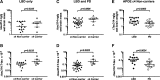
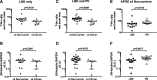
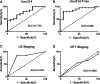
Lewy body diseases are neurodegenerative disorders characterized by Lewy bodies in the brain. Lewy body dementia (LBD) refers to two forms of Lewy body disease: Parkinson's disease with dementia (PDD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). Tau is a cytoskeletal protein found in neurofibrillary tangles, but not Lewy bodies. The gene encoding tau, MAPT, is a well-established genetic risk factor for LBD; odds ratios of the H1:H2 MAPT haplotypes have been reported in the range of 2 to 4. Despite this genetic association, the mechanism by which tau contributes to dementia is unclear. Recently, a soluble form of tau, Δtau314, which is generated when caspase-2 (Casp2) cleaves tau at Asp314, was reported to be associated with impaired cognition in mice modeling frontotemporal dementia, and with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease (AD) in humans. To investigate whether Δtau314 is associated with dementia in Lewy body disease, we compared Δtau314 levels in aqueous extracts from the superior temporal gyrus of pathologically confirmed LBD (n = 21) and non-dementia Parkinson's disease (PD) (n = 12). We excluded subjects with AD or microvascular pathology, which could mask potential associations of Δtau314 with LBD.Using a Δtau314-specific ELISA, we found ~ 2-fold higher levels of Δtau314 in LBD relative to PD (p = 0.009). Additionally, we found ~40% lower levels of soluble total tau and the neuronal marker β-III-tubulin in LBD. These results suggest that in LBD, there is substantial neuron loss or axonal degeneration in the neocortex but disproportionately high levels of Δtau314 in the surviving neurons.Our results indicate an association between Δtau314 and dementia in Lewy body disease. Cleavage of tau by Casp2 promotes the mislocalization of tau to dendritic spines leading to a reduction in postsynaptic AMPA receptors and excitatory neurotransmission, which suggests a mechanism of the synaptic dysfunction underlying cognitive impairment in LBD. These findings support the potential of Casp2 as a novel drug target for treating LBD.
Keywords: Caspase-2; Dementia; Lewy body; Parkinson’s; Tau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Carroll JB, Southwell AL, Graham RK, Lerch JP, Ehrnhoefer DE, Cao LP, Zhang WN, Deng Y, Bissada N, Henkelman RM, et al. Mice lacking caspase-2 are protected from behavioral changes, but not pathology, in the YAC128 model of Huntington disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2011;6:59. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-59. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

