[Preemptive nebulized ketamine for pain control after tonsillectomy in children: randomized controlled trial]
- PMID: 31362882
- PMCID: PMC9391877
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjan.2019.03.007
[Preemptive nebulized ketamine for pain control after tonsillectomy in children: randomized controlled trial]
Abstract
Objectives: The administration of ketamine as nebulized inhalation is relatively new and studies on nebulized ketamine are scarce. We aimed to investigate the analgesic efficacy of nebulized ketamine (1 and 2 mg.kg−1) administered 30 min before general anesthesia in children undergoing elective tonsillectomy in comparison with intravenous ketamine (0.5 mg.kg−1) and saline placebo.
Methods: One hundred children aged (7–12) years were randomly allocated in four groups (n = 25) receive; Saline Placebo (Group C), Intravenous Ketamine 0.5 mg.kg−1 (Group K-IV), Nebulized Ketamine 1 mg.kg−1 (Group K-N1) or 2 mg.kg−1 (Group K-N2). The primary endpoint was the total consumption of rescue analgesics in the first 24 h postoperative.
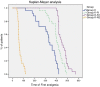
Results: The mean time to first request for rescue analgesics was prolonged in K-N1 (400.9 ± 60.5 min, 95% CI 375.9–425.87) and K-N2 (455.5 ± 44.6 min, 95% CI 437.1–473.9) groups compared with Group K-IV (318.5 ± 86.1 min, 95% CI 282.9–354.1) and Group C (68.3 ± 21.9 min, 95% CI 59.5–77.1; p < 0.001), with a significant difference between K-N1 and K-N2 Groups (p < 0.001). The total consumption of IV paracetamol in the first 24 h postoperative was reduced in Group K-IV (672.6 ± 272.8 mg, 95% CI 559.9–785.2), Group K-N1 (715.6 ± 103.2 mg, 95% CI 590.4–840.8) and Group K-N2 (696.6 ± 133.3 mg, 95% CI 558.8–834.4) compared with Control Group (1153.8 ± 312.4 mg, 95% CI 1024.8–1282.8; p < 0.001). With no difference between intravenous and Nebulized Ketamine Groups (p = 0.312). Patients in intravenous and Nebulized Ketamine Groups showed lower postoperative VRS scores compared with Group C (p < 0.001), no differences between K-IV, K-N1 or K-N2 group and without significant adverse effects.
Conclusion: Preemptive nebulized ketamine was effective for post-tonsillectomy pain relief. It can be considered as an effective alternative route to IV ketamine.
Keywords: Amigdalectomia; Analgesia; Cetamina IV; Cetamina nebulizada; Children; Crianças; IV ketamine; Nebulized ketamine; Tonsillectomy.
Copyright © 2019. Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response to: Preemptive nebulized ketamine for pain control after tonsillectomy in children: randomized controlled trial.Braz J Anesthesiol. 2020 Nov-Dec;70(6):686-687. doi: 10.1016/j.bjan.2020.10.006. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 33276978 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Nebulized Ketamine to Intravenous Subdissociative Dose Ketamine for Treating Acute Painful Conditions in the Emergency Department: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy Controlled Trial.Ann Emerg Med. 2024 Oct;84(4):354-362. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2024.03.024. Epub 2024 May 2. Ann Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38703175 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Analysis of Nebulized Versus Intravenous Fentanyl for Pain Control After Tonsillectomy: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2024 Sep;133(9):776-782. doi: 10.1177/00034894241259376. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2024. PMID: 38874203 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of different administration of ketamine and intravenous tramadol hydrochloride for postoperative pain relief and sedation after pediatric tonsillectomy.J Craniofac Surg. 2015 Jan;26(1):e21-4. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000001250. J Craniofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25569408 Clinical Trial.
-
Demonstration of analgesic effect of intranasal ketamine and intranasal fentanyl for postoperative pain after pediatric tonsillectomy.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Jan;104:182-185. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.11.018. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29287863 Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative peritonsillar lornoxicam infiltration is not superior to intravenous lornoxicam for pain relief following tonsillectomy in adults.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010 Sep;27(9):807-11. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e32833c3101. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010. PMID: 20613539 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the effects of ketamine via nebulization versus different pharmacological approaches in pediatric sedation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Nov 16;23(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02298-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37974083 Free PMC article.
-
Nebulized ketamine for managing acute pain in the pediatric emergency department: A case series.Turk J Emerg Med. 2021 Apr 9;21(2):75-78. doi: 10.4103/2452-2473.313334. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. Turk J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33969243 Free PMC article.
-
The Increased Channel Activity of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptors at Extrasynaptic Sites in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex of Neonatal Rats Following Prolonged Ketamine Exposure.J Pain Res. 2021 Aug 8;14:2381-2389. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S320674. eCollection 2021. J Pain Res. 2021. PMID: 34393508 Free PMC article.
-
A Promising Route for Established Indications: A Systematic Review of Nebulized Ketamine in Pain.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2025 Apr 30;29(1):81. doi: 10.1007/s11916-025-01394-z. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2025. PMID: 40304824
-
Response to: Preemptive nebulized ketamine for pain control after tonsillectomy in children: randomized controlled trial.Braz J Anesthesiol. 2020 Nov-Dec;70(6):686-687. doi: 10.1016/j.bjan.2020.10.006. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 33276978 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- White M.C., Nolan J.A. An evaluation of pain and postoperative nausea and vomiting following the introduction of guidelines for tonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005;15:683–688. - PubMed
-
- Hasnain F., Janbaz K.H., Qureshi M.A. Analgesic effect of ketamine and morphine after tonsillectomy in children. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2012;25:599–606. - PubMed
-
- Umuroglu T., Eti Z., Ciftci H., et al. Analgesia for adenotonsillectomy in children: a comparison of morphine, ketamine, and tramadol. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004;14:568–573. - PubMed
-
- Grainger J., Saravanappa N. Local anesthetic for post-tonsillectomy pain: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2008;33:411–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

