A Gammaherpesvirus MicroRNA Targets EWSR1 (Ewing Sarcoma Breakpoint Region 1) In Vivo To Promote Latent Infection of Germinal Center B Cells
- PMID: 31363027
- PMCID: PMC6667617
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00996-19
A Gammaherpesvirus MicroRNA Targets EWSR1 (Ewing Sarcoma Breakpoint Region 1) In Vivo To Promote Latent Infection of Germinal Center B Cells
Abstract
Gammaherpesviruses, including the human pathogens Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), directly contribute to the genesis of multiple types of malignancies, including B cell lymphomas. In vivo, these viruses infect B cells and manipulate B cell biology to establish lifelong latent infection. To accomplish this, gammaherpesviruses employ an array of gene products, including microRNAs (miRNAs). Although numerous host mRNA targets of gammaherpesvirus miRNAs have been identified, the in vivo relevance of repression of these targets remains elusive due to species restriction. Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV68) provides a robust virus-host system to dissect the in vivo function of conserved gammaherpesvirus genetic elements. We identified here MHV68 mghv-miR-M1-7-5p as critical for in vivo infection and then validated host EWSR1 (Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1) as the predominant target for this miRNA. Using novel, target-specific shRNA-expressing viruses, we determined that EWSR1 repression in vivo was essential for germinal center B cell infection. These findings provide the first in vivo demonstration of the biological significance of repression of a specific host mRNA by a gammaherpesvirus miRNA.IMPORTANCE Gammaherpesviruses, including the human pathogens Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), directly contribute to the genesis of multiple types of malignancies. In vivo, these viruses infect B cells and manipulate B cell biology to establish lifelong infection. To accomplish this, gammaherpesviruses employ an array of gene products, including miRNAs, short noncoding RNAs that bind to and repress protein synthesis from specific target mRNAs. The in vivo relevance of repression of targets of gammaherpesvirus miRNAs remains highly elusive. Here, we identified a murine gammaherpesvirus miRNA as critical for in vivo infection and validated the host mRNA EWSR1 (Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1) as the predominant target for this miRNA. Using a novel technology, we demonstrated that repression of EWSR1 was essential for in vivo infection of the critical B cell reservoir. These findings provide the first in vivo demonstration of the significance of repression of a specific host mRNA by a gammaherpesvirus miRNA.
Keywords: EWSR1; MHV68; gammaherpesvirus; in vivo; miRNA.
Copyright © 2019 Wang et al.
Figures
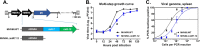
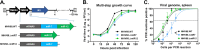
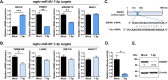
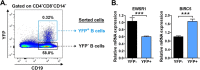


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

