Genetically diverse Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations display similar transcriptomic profiles in a cystic fibrosis explanted lung
- PMID: 31363089
- PMCID: PMC6667473
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11414-3
Genetically diverse Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations display similar transcriptomic profiles in a cystic fibrosis explanted lung
Abstract
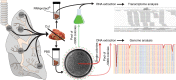
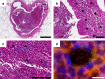
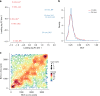
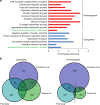
Previous studies have demonstrated substantial genetic diversification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa across sub-compartments in cystic fibrosis (CF) lungs. Here, we isolate P. aeruginosa from five different sampling areas in the upper and lower airways of an explanted CF lung, analyze ex vivo transcriptional profiles by RNA-seq, and use colony re-sequencing and deep population sequencing to determine the genetic diversity within and across the various sub-compartments. We find that, despite genetic variation, the ex vivo transcriptional profiles of P. aeruginosa populations inhabiting different regions of the CF lung are similar. Although we cannot estimate the extent to which the transcriptional response recorded here actually reflects the in vivo transcriptomes, our results indicate that there may be a common in vivo transcriptional profile in the CF lung environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Frimmersdorf E, Horatzek S, Pelnikevich A, Wiehlmann L, Schomburg D. How Pseudomonas aeruginosa adapts to various environments: a metabolomic approach. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;12:1734–1747. - PubMed
-
- de Bentzmann S, Plesiat P. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa opportunistic pathogen and human infections. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;13:1655–1665. - PubMed
-
- Gellatly SL, Hancock RE. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: new insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog. Dis. 2013;67:159–173. - PubMed
-
- Valentini M, Gonzalez D, Mavridou DA, Filloux A. Lifestyle transitions and adaptive pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018;41:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

