The language context effect in facial expressions processing and its mandatory characteristic
- PMID: 31363107
- PMCID: PMC6667436
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-47075-x
The language context effect in facial expressions processing and its mandatory characteristic
Abstract
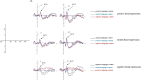
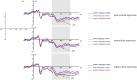
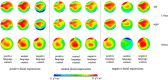
Background visual scenes in which faces are perceived provide contextual information for facial expression processing. One type of background information, the language context, has a vital influence on facial expression processing. The current study is aimed to investigate the effect of the language context on facial expression processing by recording event-related potentials (ERPs). Experiment one adopted the facial expression categorization task to investigate the effects of different language contexts on emotional and non-emotional facial processing. Experiment two adopted the task-irrelevant paradigm to investigate whether the language context effect on facial expression processing was mandatory. The results found that (1) the language context affected facial expression processing. Facial expression processing was promoted when the language context was emotionally congruent with faces. Moreover, the language context had an evoking effect on neutral faces. To be detailed, neutral facial expressions were evoked to be judged as positive in the positive language context while as negative in the negative language context. (2) The language context effect still affected facial expression processing in a task-irrelevant paradigm. When the language context was emotionally incongruent with facial expressions, larger N170 and LPP amplitudes were elicited, indicating the inhibition of incongruent emotions. These findings prove that the language context effect on facial expression processing is mandatory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early and late temporo-spatial effects of contextual interference during perception of facial affect.Int J Psychophysiol. 2009 Oct;74(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2009.05.010. Epub 2009 May 24. Int J Psychophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19470392
-
Emotional conflict in facial expression processing during scene viewing: an ERP study.Brain Res. 2015 May 22;1608:138-46. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.02.047. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25747865
-
Visual processing in a facial emotional context: an ERP study.Int J Psychophysiol. 2009 Jan;71(1):25-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2008.07.017. Epub 2008 Jul 30. Int J Psychophysiol. 2009. PMID: 18771695
-
Facial Expressions in Context: Electrophysiological Correlates of the Emotional Congruency of Facial Expressions and Background Scenes.Front Psychol. 2017 Dec 12;8:2175. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02175. eCollection 2017. Front Psychol. 2017. PMID: 29312049 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Bias by Gender Interaction on N170 Response to Emotional Facial Expressions in Major and Minor Depression.Brain Topogr. 2016 Mar;29(2):232-42. doi: 10.1007/s10548-015-0444-4. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Brain Topogr. 2016. PMID: 26239020
Cited by
-
Semantic and syntactic processing of emojis in sentential intermediate positions.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Aug;18(4):1743-1752. doi: 10.1007/s11571-023-10037-1. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 39104667 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of emotion words activation and satiation on facial expression perception: evidence from behavioral and ERP investigations.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jul 31;14:1192450. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1192450. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37588024 Free PMC article.
-
Facial emotion processing and language during early-to-middle childhood development: An event related potential study.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022 Feb;53:101052. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2021.101052. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34954666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu HY, et al. The influence of emotional context on rating of facial expressions. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2016;24:204–206. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2016.02.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

