QUALITY OF LIFE IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS - A PRELIMINARY STUDY
- PMID: 31363338
- PMCID: PMC6629210
- DOI: 10.20471/acc.2019.58.01.20
QUALITY OF LIFE IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS - A PRELIMINARY STUDY
Abstract
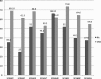
The most severe effects of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are loss of physical function and chronic pain, which may have a major impact on different areas of the person's existence. The aim of this study was to get an insight into the quality of life (QOL) in subjects with RA in connection with pain perception and functional ability. The following instruments were used: the World Health Organization Quality of Life Questionnaire (WHOQOL-BREF), Short Form Health Survey (SF-36), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain). The results indicated that there was no statistical difference in the QOL between subjects with RA and healthy population according to SF-36 Croatian norms. Also, the results showed that stronger pain experience was significantly associated with poorer social functioning assessment (SF36SF, Spearman's rho=-0.463, p<0.05), poorer general health perception (SF36GH, Spearman's rho=-0.432, p<0.05) and poorer physical functioning (WHOPH, Spearman's rho=-0.688, p<0.01). Furthermore, the subjects evaluating their general functional state worse were found to have worse physical functioning (SF36PF, Spearman's rho=-0.699 and WHOPH, Spearman's rho=-0.769), poorer social functioning (SF36SF, Spearman's rho=-0.580) and experienced greater pain intensity (SF36BP, Spearman's rho=-0.652). Therefore, additional efforts should be invested to define a holistic and integrative model of treatment and rehabilitation of people with RA, focused on pain relief, improvement of functional ability, encouraging social interaction and supporting positive emotional responses.
Keywords: Activities of daily living; Arthritis, rheumatoid; Health status; Pain; Quality of life.
Figures
References
-
- Jajić I. Reumatologija. Priručnik za liječnike specijaliste reumatologije, specijaliste drugih graničnih struka i studente medicine. Zagreb: Medicinska knjiga, 1995. (in Croatian)
-
- Gibofsky A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Manag Care. 2012. Dec 18; 13(Suppl):S295–302. - PubMed
-
- Fassbender HG. The clinical presentation of rheumatoid arthritis: the results from three separate pathogenetic mechanisms in adults and children. Acta Clin Croat. 2008;47(1):50–5.
-
- Vlak T. Utjecaj reumatoidnog artritisa na radnu sposobnost bolesnika. Reumatizam. 2001;48(1):12–8. [in Croatian] - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
