HSP70 silencing aggravates apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation in vitro
- PMID: 31363363
- PMCID: PMC6614734
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7697
HSP70 silencing aggravates apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation in vitro
Abstract
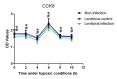
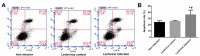
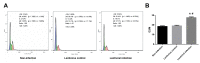
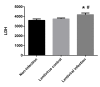
Lung ischemia-reperfusion can cause acute lung injury, which is closely associated with apoptosis. Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) is an anti-apoptotic protein that promotes cell survival under a variety of different stress conditions. However, the role and mechanism of HSP70 in lung ischemia-reperfusion injury is yet to be fully elucidated. In the present study, an in vitro hypoxia/reoxygenation model of A549 cells was established to simulate lung ischemia-reperfusion and HSP70 was silenced by transfecting A549 cells with an shRNA sequence targeting HSP70. Western blotting, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction, Cell Counting kit-8 and flow cytometry were used to detect protein levels, RNA expression, cell activity and apoptosis. The results revealed that silencing HSP70 reduced cell viability, aggravated apoptosis, increased lactate dehydrogenase levels and induced a G2/M blockade in a hypoxia-reoxygenation A549 cell model. Furthermore, silencing HSP70 decreased the phosphorylation levels of protein kinase B (AKT) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK); however, the total AKT and ERK levels did not change significantly. Pretreating A549 cells with the AKT pathway inhibitor, LY294002 and the ERK pathway inhibitor, U0216 led to a decrease in HSP70 expression. These results indicate that silencing HSP70 may aggravate apoptosis in hypoxia-reoxygenation cell models, potentially via the mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathways.
Keywords: apoptosis; extracellular signal-regulated kinase; heat shock protein 70; hypoxia; mitogen-activated protein kinase; phosphoinositide 3-kinase; protein kinase B; reoxygenation.
Figures

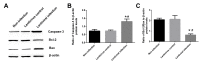
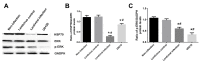
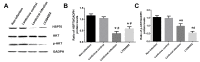
Similar articles
-
HSP70 inhibition suppressed glioma cell viability during hypoxia/reoxygenation by inhibiting the ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021 Aug;53(4):405-413. doi: 10.1007/s10863-021-09904-5. Epub 2021 Aug 7. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 34363569
-
Remifentanil preconditioning protects rat cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury via δ-opioid receptor mediated activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 15;789:395-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27492364
-
Signal transduction of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt activation by hypoxia/reoxygenation in renal epithelial cells.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;85(11):1189-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Jul 24. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16860436
-
Renal tubular cell death and inflammation response are regulated by the MAPK-ERK-CREB signaling pathway under hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019 Oct-Dec;39(5-6):383-391. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2019.1698050. Epub 2019 Nov 29. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019. PMID: 31782334 Review.
-
Protection of teprenone against hypoxia and reoxygenation stress in stomach and intestine of Lateolabrax maculatus.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2020 Apr;46(2):575-584. doi: 10.1007/s10695-019-00732-4. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31900796 Review.
Cited by
-
Heat Shock Protein-70 Levels Are Associated With a State of Oxidative Damage in the Development of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.Front Pediatr. 2021 May 26;9:616452. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.616452. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34123957 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Reduces Kidney Injury in a Rat Model of Uremia and is Associated with Increased Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70).Med Sci Monit. 2020 Feb 10;26:e919086. doi: 10.12659/MSM.919086. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32040471 Free PMC article.
-
Maize heat shock proteins-prospection, validation, categorization and in silico analysis of the different ZmHSP families.Stress Biol. 2023 Sep 6;3(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s44154-023-00104-2. Stress Biol. 2023. PMID: 37981586 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury-induced apoptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cells through miR-21-5p.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):7747-7754. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1982845. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34617873 Free PMC article.
-
Bag-1L Protects against Cell Apoptosis in an In Vitro Model of Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through the C-Terminal "Bag" Domain.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Mar 17;2021:8822807. doi: 10.1155/2021/8822807. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34056003 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
