MicroRNA-873 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer cells by directly targeting hepatoma-derived growth factor
- PMID: 31363373
- PMCID: PMC6614730
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7713
MicroRNA-873 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer cells by directly targeting hepatoma-derived growth factor
Retraction in
-
MicroRNA-873 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer cells by directly targeting hepatoma-derived growth factor.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun 27;24(2):538. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11475. eCollection 2022 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35837040 Free PMC article.
Abstract
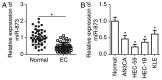
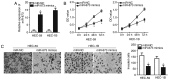
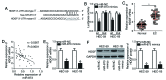
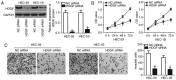
An accumulation of evidence has demonstrated that abnormal microRNA (miRNA or miR) expression is associated with different types of cancer, including endometrial cancer (EC). The dysregulation of miRNAs may serve important roles in the development and progression of EC by regulating multiple aggressive biological behaviors, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis and angiogenesis. An in-depth understanding of the miRNAs associated with EC initiation and progression may be crucial for identifying successful therapeutic techniques. miR-873 has been demonstrated to be dysregulated in different types of cancer. However, the expression status and regulatory roles of miR-873 are yet to be elucidated in EC. In the present study, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was carried out to detect miR-873 expression in EC tissues and cell lines. Cell Counting Kit-8 and in vitro invasion assays were utilized to determine the influence of miR-873 on the proliferation and invasion of EC cells. miR-873 expression was revealed to be downregulated in EC tissues and cell lines. Decreased miR-873 expression was significantly associated with International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage and lymph node metastasis of patients with EC. Functional assays revealed that resumed miR-873 expression suppressed the proliferation and invasion of EC cells. Additionally, hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF) was indicated to be a direct target gene of miR-873 in EC cells. HDGF was highly expressed in EC tissues and inversely correlated with miR-873 expression. HDGF silencing also imitated the tumor-suppressor activity of miR-873 overexpression in EC cells. A series of rescue experiments identified that recovered HDGF expression hindered the anti-proliferative and anti-invasive roles of miR-873 upregulation in EC cells. In conclusion, the present study indicated that miR-873 serves an important role as a tumor suppressor in EC development by directly targeting HDGF. The results may provide a novel insight into clinical treatments, which can be used to prevent EC aggression.
Keywords: endometrial cancer; hepatoma-derived growth factor; invasion; microRNA-873; proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of miRNAs in the Regulation of Endometrial Cancer Invasiveness and Metastasis-A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 6;13(14):3393. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143393. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-939 Directly Targets HDGF to Inhibit the Aggressiveness of Prostate Cancer via Deactivation of the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 18;13:4257-4270. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S250101. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Oct 05;14:5001-5002. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S341951. PMID: 32547060 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MicroRNA-139-5p inhibits cell viability, migration and invasion and suppresses tumor growth by targeting HDGF in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Mar;19(3):1806-1814. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11296. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Oncol Lett. 2020. Retraction in: Oncol Lett. 2023 Oct 09;26(6):503. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14090. PMID: 32194674 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MicroRNA-432 is downregulated in cervical cancer and directly targets FN1 to inhibit cell proliferation and invasion.Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):1475-1482. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10403. Epub 2019 May 27. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31423213 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and clinical applications of interleukins in endometrial carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:1001693. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1001693. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531027 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor: An Overview and Its Role as a Potential Therapeutic Target Molecule for Digestive Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 13;21(12):4216. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124216. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32545762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicorRNA-148b inhibits cell proliferation and facilitates cell apoptosis by regulating DNA Methyltransferase 1 in endometrial cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(2):1100-1112. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.12.79. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117454 Free PMC article.
-
[MicroRNA-145-5p over-expression suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion and promotes apoptosis of human endometrial cancer cells by targeting dual specific phosphatase 6].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Jan 30;40(1):61-66. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.01.10. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32376567 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Computational and Bioinformatics Methods for MicroRNA Gene Prediction.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2257:349-373. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1170-8_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34432287
-
The Role of miRNAs in the Regulation of Endometrial Cancer Invasiveness and Metastasis-A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 6;13(14):3393. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143393. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
