Levofloxacin-containing triple therapy versus bismuth-based quadruple therapy as regimens for second line anti- Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 31363400
- PMCID: PMC6619475
- DOI: 10.22088/cjim.10.2.211
Levofloxacin-containing triple therapy versus bismuth-based quadruple therapy as regimens for second line anti- Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
Background: Although the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection decreased following the hygiene promotion and application of proper anti- H.pylori treatments, unfortunately gradual increase is reported in treatment failure; hence, application of a proper treatment regimen as a second-line therapy is of great importance.
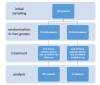
Methods: In the current randomized, clinical trial, a total of 120 patients with peptic ulcers who failed to respond to treatment were enrolled. In the OLA group, a regimen of omeprazole 40 mg/day, levofloxacin 1 g/day, and amoxicillin 2 g/ day was prescribed; however, a regimen of omeprazole 40 mg/day, bismuth sub-citrate 480 mg/day, furazolidone 400 mg/day, and amoxicillin 2 g/day was administered to the OFAB group. Both groups were treated for 2 weeks, and 6 weeks after the treatment, the urea breath test (UBT) was performed in the subjects. Collected data were analyzed with SPSS Version 18. At the end, 58 patients in group OLA and 57 patients in the OFAB group were analyzed.
Results: According to the results of the current study, 96.7% of the subjects in the OLA and 95% in the OFAB groups completed the treatment course and the eradication rates were 86.7% and 78.3% in the OLA and OFAB groups, respectively (P=0.23). Treatment side effects were observed in 51.7% and 11.7% of the subjects in the OLA and OFAB groups, respectively (P<0.01).
Conclusion: Both regimens were applicable as the second-line therapy due to insignificant difference between the results of the 2 groups; however, OLA regimen was superior to OFAB, due to lower side effects.
Keywords: Bismuth-based quadruple therapy; Helicobacter pylori; Levofloxacin-based triple therapy; Second-line Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori second-line rescue therapy with levofloxacin- and bismuth-containing quadruple therapy, after failure of standard triple or non-bismuth quadruple treatments.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(8):768-75. doi: 10.1111/apt.13128. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25703120 Clinical Trial.
-
Second-line rescue treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Where are we now?World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Oct 28;24(40):4548-4553. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4548. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30386104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Second-line rescue triple therapy with levofloxacin after failure of non-bismuth quadruple "sequential" or "concomitant" treatment to eradicate H. pylori infection.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jun;48(6):652-6. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2013.786132. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23556551 Clinical Trial.
-
Furazolidone, amoxicillin and omeprazole with or without bismuth for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer disease.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2011 Feb;22(1):1-5. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21480103 Clinical Trial.
-
A new look at anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep 21;17(35):3971-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i35.3971. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22046084 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Levofloxacin Quadruple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Dec 6;2022:9794901. doi: 10.1155/2022/9794901. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36523418 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in Iran: A Review.Middle East J Dig Dis. 2024 Jul;16(3):147-154. doi: 10.34172/mejdd.2024.389. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2024. PMID: 39386340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of tailored second-line therapy of Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with clarithromycin-based treatment failure: a multicenter prospective study.Gut Pathog. 2020 Aug 29;12:39. doi: 10.1186/s13099-020-00378-1. eCollection 2020. Gut Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32874206 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Effect of Two Low-dose and High-dose Four-drug Regimens of Furazolidone in Eradicating Helicobacter Pylori.Middle East J Dig Dis. 2021 Apr;13(2):131-138. doi: 10.34172/mejdd.2021.216. Epub 2021 May 29. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2021. PMID: 34712451 Free PMC article.
-
First-Line Levofloxacin-Based Triple Therapy Versus Standard Bismuth-Based Quadruple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication in Saudi Arabia: A Retrospective Single-Center Study.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 5;8(2):e70432. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70432. eCollection 2025 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39917596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiesa C, Pacifico L, Anania C, et al. Helicobacter pylori therapy in children: overview and challenges. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2010;23:405–16. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki H, Franceschi F, Nishizawa T, Gasbarrini A. Extragastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2011;16:65–9. - PubMed
-
- Zamani M, Ebrahimtabar F, Zamani V, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47:868–876. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources