A rare presentation of spontaneous atheroembolic renal disease: A case report
- PMID: 31363463
- PMCID: PMC6656662
- DOI: 10.5527/wjn.v8.i3.67
A rare presentation of spontaneous atheroembolic renal disease: A case report
Abstract
Background: Atheroembolic renal disease (AERD) is caused by occlusion of the small renal arteries from embolized cholesterol crystals arising from ulcerated atherosclerotic plaques. This usually manifests as isolated renal disease or involvement from systemic atheroembolic disease. Here we report a case of AERD that responded well to steroid therapy.
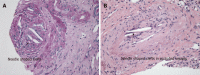
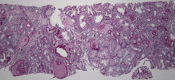
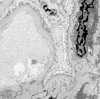
Case summary: A 62-year-old woman with a history of hypertension and stage IIIa chronic kidney disease was referred for rapidly worsening renal function over a 4-mo period. She complained of swollen legs, dyspnea on exertion, and two episodes of epistaxis about a month prior to admission. She reported no history of invasive vascular procedures, use of radio contrast agents, or treatment with anticoagulants or thrombolytic agents. Urinalysis showed a few red blood cells and granular casts. Serology was positive for cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (c-ANCA). Non-contrast-enhanced computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis showed diffuse atherosclerotic changes in the aortic arch. Thus, c-ANCA-associated vasculitis was suspected, and the patient was started on pulse intravenous methylprednisolone. Her renal biopsy showed evidence of AERD. She was discharged with oral prednisone, and her renal function continued to improve during the initial follow-up.
Conclusion: In cases of non-vasculitis-associated ANCA, a high degree of clinical suspicion is required to pursue the diagnosis of spontaneous AERD in patients with clinical or radiological evidence of atherosclerotic burden. Although no specific treatment is available, the potential role of statins and steroids requires exploration.
Keywords: Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies associated vasculitis; Atheroembolic renal disease; Case report; Chronic kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atheroembolic Kidney Disease.2024 Jun 22. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 22. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 29494024 Free Books & Documents.
-
Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody following cimetidine treatment: a case report.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Aug 30;22(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02502-y. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34461843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atheroembolic Renal Disease: A Case Series.Indian J Nephrol. 2019 Nov-Dec;29(6):427-430. doi: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_265_18. Indian J Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31798227 Free PMC article.
-
[Diffuse panbronchiolitis with myeloperoxidase-specific antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-related vasculitis].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 1998 May;36(5):453-8. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9742863 Japanese.
-
[Atheroembolism renal disease: diagnosis and etiologic factors].Clin Ter. 2012 Jul;163(4):313-22. Clin Ter. 2012. PMID: 23007816 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
The Controversial Role of Glucocorticoids in Atheroembolic Renal Disease: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 27;13(21):6441. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216441. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scolari F, Ravani P, Gaggi R, Santostefano M, Rollino C, Stabellini N, Colla L, Viola BF, Maiorca P, Venturelli C, Bonardelli S, Faggiano P, Barrett BJ. The challenge of diagnosing atheroembolic renal disease: clinical features and prognostic factors. Circulation. 2007;116:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Scolari F, Ravani P. Atheroembolic renal disease. Lancet. 2010;375:1650–1660. - PubMed
-
- Scolari F, Ravani P, Pola A, Guerini S, Zubani R, Movilli E, Savoldi S, Malberti F, Maiorca R. Predictors of renal and patient outcomes in atheroembolic renal disease: a prospective study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:1584–1590. - PubMed
-
- Modi KS, Rao VK. Atheroembolic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:1781–1787. - PubMed
-
- Pasupala U, Soare M, Dianne S, Paixao R, Fromkin B, Berho M, Braun M. Atheroembolic Renal Disease and Anticoagulants use: A Case Report and Literature Review. World J Nephrol Urol. 2012;I:115–117.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

