Relationship between circulating irisin levels and overweight/obesity: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 31363472
- PMCID: PMC6656672
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1444
Relationship between circulating irisin levels and overweight/obesity: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Currently, the findings about irisin as a novel myokine related to obesity are inconsistent in overweight/obese people. To our knowledge, no systematic analysis has been conducted to evaluate the relationship between irisin levels and overweight/obesity.
Aim: To evaluate the association between circulating irisin levels and overweight/obesity.
Methods: The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, SCOPUS, and the ISI Web of Science were searched to retrieve all of the studies associated with circulating irisin levels and overweight/obesity. Standard mean difference values and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were estimated and pooled using meta-analysis methodology.
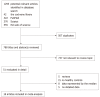
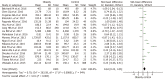
Results: A total of 18 studies were included in our meta-analysis containing 1005 cases and 1242 controls. Our analysis showed that the circulating irisin level in overweight/obese people was higher than that in overall healthy controls (random effects MD = 0.63; 95%CI: 0.22-1.05; P = 0.003). In the subgroup analysis by ethnicity, the irisin level was higher in overweight/obesity people than that in controls in Africa (random effects MD = 3.41; 95%CI: 1.23-5.59; P < 0.05) but not in European, Asian, or American populations. In addition, in a subgroup analysis by age, the results showed that obese children exhibited a higher irisin level than controls (random effects MD = 0.86; 95%CI: 0.28-1.43; P < 0.05).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis provides evidence that circulating irisin is higher in obese individuals compared to healthy controls and it is important to identify the relationship between circulating irisin levels and overweight/obesity in predicting overweight/obesity.
Keywords: Body mass index; Irisin; Myokines; Overweight/obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- van der Klaauw AA, Farooqi IS. The hunger genes: pathways to obesity. Cell. 2015;161:119–132. - PubMed
-
- Ryan DH, Kahan S. Guideline Recommendations for Obesity Management. Med Clin North Am. 2018;102:49–63. - PubMed
-
- Kushner RF, Kahan S. Introduction: The State of Obesity in 2017. Med Clin North Am. 2018;102:1–11. - PubMed
-
- El-Lebedy DH, Ibrahim AA, Ashmawy IO. Novel adipokines vaspin and irisin as risk biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018;12:643–648. - PubMed
-
- Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD, Efstathiadou ZA, Makras P, Perakakis N, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS. Irisin in metabolic diseases. Endocrine. 2018;59:260–274. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

