Cirrhosis complicating Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: A case report
- PMID: 31363473
- PMCID: PMC6656663
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1456
Cirrhosis complicating Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: A case report
Abstract
Background: The features of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) include exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, skeletal abnormalities and bone marrow dysfunction; an often overlooked feature is hepatic involvement.
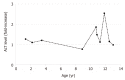
Case summary: We report a child who initially presented with failure to thrive and mildly elevated transaminase levels and was determined to have pancreatic insufficiency due to SDS. During follow-up he had persistently elevated transaminase levels and developed hepatosplenomegaly. An investigation was performed to determine the etiology of ongoing liver injury, including a liver biopsy which revealed hepatic cirrhosis.
Conclusion: Cirrhosis has rarely been reported with SDS. While many of the hepatic disorders associated with SDS improve with age, there are rare exceptions with serious implications for long-term outcome.
Keywords: Case report; Cirrhosis; Liver dysfunction; Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Kusick VA. Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome; SDS. Omim, 4 June 1986. web. 3 May 2017
-
- Shwachman H, Diamond LK, Oski FA, Khaw KT. The syndrome of pancreatic insufficiency and bone marrow dysfunction. J Pediatr. 1964;65:645–663. - PubMed
-
- Bodian M, Sheldon W, Lightwood R. Congenital hypoplasia of the exocrine pancreas. Acta Paediatr. 1964;53:282–293. - PubMed
-
- Liebman WM, Rosental E, Hirshberger M, Thaler MM. Shwachman-Diamond sydnrome and chronic liver disease. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1979;18:695–696, 698. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources