Removal of pediatric stage IV neuroblastoma by robot-assisted laparoscopy: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 31363479
- PMCID: PMC6656671
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1499
Removal of pediatric stage IV neuroblastoma by robot-assisted laparoscopy: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Neuroblastoma (NB) is the most common extracranial solid tumor in children, with an incidence of approximately 1/10000. Surgical resection is an effective treatment for children with NB. Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery is a new method and is superior to conventional laparoscopic surgery, since it has been preliminarily applied in clinical practice with a significant curative effect. This paper discusses significance and feasibility of complete resection of stage IV NB using robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery, while comparing its safety and effectiveness with conventional laparoscopic surgery.
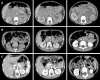
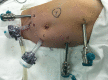
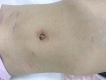
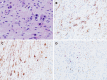
Case summary: In June 2018, a girl with stage IV retroperitoneal NB, aged 3 years and 5 mo, was admitted. Her weight was 15 kg, and her height was 100 cm. Robot-assisted, five-port laparoscopic resection of NB was performed. Starting from the middle point between the navel and the anterior superior iliac spine to the left lower abdomen, the pneumoperitoneum and observation hole (10 mm) were established using the Hasson technique. Operation arm #1 was located between the left anterior axillary line, the navel, and the costal margin (8 mm); operation arm #2 was located at the intersection of the right anterior axillary line and Pfannenstiel line (8 mm); one auxiliary hole was located between arm #2 (on the Pfannenstiel line) and the observation hole (12 mm); and another auxiliary hole (5 mm) was located slightly below the left side of the xiphoid. Along the right line of Toldt and the hepatic flexure of the transverse colon, the colon was turned to the left and below with a hook electrode. Through Kocher's incision, the duodenum and the pancreatic head were turned to the left to expose the inferior vena cava and the abdominal aorta. The vein was separated along the right external iliac, and the inferior vena cava was then lifted to expose the right renal vein from the bottom to the top. The tumor was transected horizontally below the renal vein, and it was first cut into pieces and then resected. The right renal artery and the left renal vein were also exposed, and the retrohepatic inferior vena cava was isolated. The tumor was resected along the surface of the psoas muscle, the back of the inferior vena cava, and the right side of the abdominal aorta. Finally, the lymph node metas-tases in front of the abdominal aorta and left renal vein were completely removed. The specimens were loaded into a disposable specimen retrieval bag and removed from the enlarged auxiliary hole. T-tube drainage was placed and brought out through a hole in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen. The operative time was 389 min, the time of pneumoperitoneum was 360 min, the intraoperative blood loss was approximately 200 mL, and the postoperative recovery was smooth. There were no complications, such as lymphatic fistula, diarrhea, bleeding, and paralytic ileus. Two months after discharge, there were no other complications. The literature on the application of robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery in the treatment of NB in children was reviewed.
Conclusion: The robot has the advantages of a three-dimensional view and flexible operation, and it can operate finely along blood vessels. The successful experience of this case confirmed that robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery can skeletonize the abdominal blood vessels in the tumor and cut the tumor into pieces, indicating that robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery is feasible.
Keywords: Case report; Children; Retroperitoneal neuroblastoma; Robot-assisted surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Uwaydah NI, Jones A, Elkaissi M, Yu Z, Palmer BW. Pediatric robot-assisted laparoscopic radical adrenalectomy and lymph-node dissection for neuroblastoma in a 15-month-old. J Robot Surg. 2014;8:289–293. - PubMed
-
- Guan R, Chen Y, Yang K, Ma D, Gong X, Shen B, Peng C. Clinical efficacy of robot-assisted versus laparoscopic liver resection: a meta analysis. Asian J Surg. 2019;42:19–31. - PubMed
-
- van der Sluis PC, van Hillegersberg R. Robot assisted minimally invasive esophagectomy (RAMIE) for esophageal cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2018;36-37:81–83. - PubMed
-
- Niu X, Yu B, Yao L, Tian J, Guo T, Ma S, Cai H. Comparison of surgical outcomes of robot-assisted laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy versus laparoscopic and open resections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J Surg. 2019;42:32–45. - PubMed
-
- Zhao W, Liu C, Li S, Geng D, Feng Y, Sun M. Safety and efficacy for robot-assisted versus open pancreaticoduodenectomy and distal pancreatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Oncol. 2018;27:468–478. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

