Mechanism of action of antimicrobial peptide P5 truncations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 31363941
- PMCID: PMC6667604
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-019-0843-0
Mechanism of action of antimicrobial peptide P5 truncations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
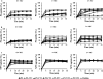
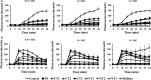
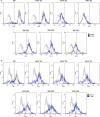
Rates of microbial drug resistance are increasing worldwide; therefore, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are considered promising alternative therapeutic agents to antibiotics. AMPs are essential components of the innate immune system and exhibit broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. P5 is a Cecropin A-Magainin 2 hybrid analog peptide with antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. In the present study, truncated peptides were designed to reduction length, retainment their antimicrobial activity and low toxicity at high concentrations compared with that of the parent peptide P5. The truncated peptides P5-CT1 and P5-NT1 exhibited antibacterial activities against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. In contrast, P5-CT2, P5-CT3, P5-NT2, and P5-NT3 showed higher antibacterial activities against gram-positive bacteria compared to Gram-negative bacteria at low concentration of peptides. The truncated peptides showed lower hemolytic activity and toxic effects against mammalian cells compared with those of the parent peptide P5. The levels of several truncated peptides were maintained in the presence of physiological concentrations of salts, indicating their high stability. The results of flow cytometry, propidium iodide uptake, n-phenyl-1-naphthylamine uptake, and 3,3'-dipropylthiadicarbocyanine iodide assays showed that these truncated peptides killed microbial cells by increasing membrane permeability, thereby causing membrane damage. The results suggested that truncated peptides of P5 have good potential for use as novel antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: Anti-biofilm; Antimicrobial peptide; Mechanism of action; Truncated peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synergistic and antibiofilm activity of the antimicrobial peptide P5 against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019 Jul 1;1861(7):1329-1337. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 31095945
-
Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity, and mechanism of action of pleurocidin against drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microb Pathog. 2019 Feb;127:70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.052. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30508627
-
Ab initio Designed Antimicrobial Peptides Against Gram-Negative Bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 16;12:715246. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.715246. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34867843 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial peptides as potential anti-biofilm agents against multidrug-resistant bacteria.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017 Aug;50(4):405-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2016.12.005. Epub 2017 Jun 26. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017. PMID: 28690026 Review.
-
Overview of ribosomal and non-ribosomal antimicrobial peptides produced by Gram positive bacteria.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017 Oct 31;63(10):20-32. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2017.63.10.4. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017. PMID: 29096754 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia Illucens) against a Selection of Human Pathogens.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0166421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01664-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 34985302 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Mechanism of Antimicrobial Peptide Bomidin and Its Safety for Macrobrachium rosenbergii.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022 Feb;14(1):169-179. doi: 10.1007/s12602-021-09857-6. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022. PMID: 34642879
-
Deciphering the Antibacterial Role of Peptide From Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii Ba49 Against Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 19;12:708712. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.708712. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34489898 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo antibiofilm activity of the synthetic antimicrobial peptide WLBU2 against multiple drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.BMC Microbiol. 2023 May 15;23(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02886-x. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37183241 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Design of Stapled Antimicrobial Peptides to Enhance Stability and In Vivo Potency against Polymicrobial Sepsis.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Mar 6;11(2):e0385322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03853-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36877022 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

