Application of a long short-term memory neural network: a burgeoning method of deep learning in forecasting HIV incidence in Guangxi, China
- PMID: 31364559
- PMCID: PMC6518582
- DOI: 10.1017/S095026881900075X
Application of a long short-term memory neural network: a burgeoning method of deep learning in forecasting HIV incidence in Guangxi, China
Abstract
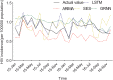
Guangxi, a province in southwestern China, has the second highest reported number of HIV/AIDS cases in China. This study aimed to develop an accurate and effective model to describe the tendency of HIV and to predict its incidence in Guangxi. HIV incidence data of Guangxi from 2005 to 2016 were obtained from the database of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network models, autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models, generalised regression neural network (GRNN) models and exponential smoothing (ES) were used to fit the incidence data. Data from 2015 and 2016 were used to validate the most suitable models. The model performances were evaluated by evaluating metrics, including mean square error (MSE), root mean square error, mean absolute error and mean absolute percentage error. The LSTM model had the lowest MSE when the N value (time step) was 12. The most appropriate ARIMA models for incidence in 2015 and 2016 were ARIMA (1, 1, 2) (0, 1, 2)12 and ARIMA (2, 1, 0) (1, 1, 2)12, respectively. The accuracy of GRNN and ES models in forecasting HIV incidence in Guangxi was relatively poor. Four performance metrics of the LSTM model were all lower than the ARIMA, GRNN and ES models. The LSTM model was more effective than other time-series models and is important for the monitoring and control of local HIV epidemics.
Keywords: ARIMA model; HIV; LSTM model; incidence; prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
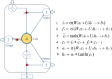
 are created by Tanh to determine which new information is stored in the unit state to update the old unit state, and turn into the new unit state (ct). Finally, cell state information is filtered with the output gate (ot) to update the hidden state (ht), which is the output of the LSTM cell.
are created by Tanh to determine which new information is stored in the unit state to update the old unit state, and turn into the new unit state (ct). Finally, cell state information is filtered with the output gate (ot) to update the hidden state (ht), which is the output of the LSTM cell.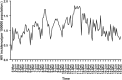

References
-
- China CDC et al. (2018) Update on the AIDS/STD epidemic in China in January, 2018. Chinese Journal of AIDS & STD 24, 219.
-
- WHOCSR (2004) WHO Recommended Surveillance Standards, 2nd Edn. WHO; Available at http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/surveillance/whocdscsrisr9... (Accessed 17 June 2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

