Estimating prevalence from dried blood spots without using biological cut-offs: application of a novel approach to hepatitis C virus in drug users in France (ANRS-Coquelicot survey)
- PMID: 31364569
- PMCID: PMC6625185
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268819001043
Estimating prevalence from dried blood spots without using biological cut-offs: application of a novel approach to hepatitis C virus in drug users in France (ANRS-Coquelicot survey)
Abstract
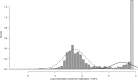
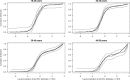
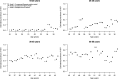
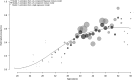
Seroprevalence estimation using cross-sectional serosurveys can be challenging due to inadequate or unknown biological cut-off limits of detection. In recent years, diagnostic assay cut-offs, fixed assay cut-offs and more flexible approaches as mixture modelling have been proposed to classify biological quantitative measurements into a positive or negative status. Our objective was to estimate the prevalence of anti-HCV antibodies among drug users (DU) in France in 2011 using a biological test performed on dried blood spots (DBS) collected during a cross-sectional serosurvey. However, in 2011, we did not have a cut-off value for DBS. We could not use the values for serum or plasma, knowing that the DBS value was not necessarily the same. Accordingly, we used a method which consisted of applying a two-component mixture model with age-dependent mixing proportions using penalised splines. The component densities were assumed to be log-normally distributed and were estimated in a Bayesian framework. Anti-HCV prevalence among DU was estimated at 43.3% in France and increased with age. Our method allowed us to provide estimates of age-dependent prevalence using DBS without having a specified biological cut-off value.
Keywords: Cut-off; drug users; hepatitis C virus; mixture model; prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Soulier A et al. (2015) Dried blood spots: a tool to ensure broad access to hepatitis C screening, diagnosis, and treatment monitoring. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 213, 1087–1095. - PubMed
-
- Tuaillon E et al. (2010) Dried blood spot for hepatitis C virus serology and molecular testing. Hepatology 51, 752–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

