Long non‑coding RNAs in lung cancer: Regulation patterns, biologic function and diagnosis implications (Review)
- PMID: 31364742
- PMCID: PMC6685594
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4850
Long non‑coding RNAs in lung cancer: Regulation patterns, biologic function and diagnosis implications (Review)
Abstract
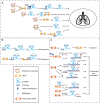
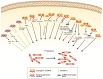
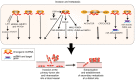
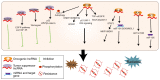
Lung cancer is the most common malignancy with the highest mortality worldwide. Emerging research has demonstrated that long non‑coding RNAs (lncRNAs), a key genomic product, are commonly dysregulated in lung cancer and have significant functions in lung cancer initiation, progression and therapeutic response. lncRNAs may interact with DNA, RNA or proteins, as tumor suppressor genes or oncogenes, to regulate gene expression and cell signaling pathways. In the present review, first a summary was presented of the causal effects of dysregulated lncRNAs in lung cancer. Next, the function and specific mechanisms of lncRNA‑mediated tumorigenesis, metastasis and drug resistance in lung cancer were discussed. Finally, the potential roles of lncRNAs as biomarkers for lung cancer were explored.
Figures
References
-
- Behera M, Owonikoko TK, Gal AA, Steuer CE, Kim S, Pillai RN, Khuri FR, Ramalingam SS, Sica GL. Lung adenocarcinoma staging using the 2011 IASLC/ATS/ERS classification: A pooled analysis of adenocarcinoma in situ and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma. Clin Lung Cancer. 2016;17:e57–e64. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2016.03.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

