Integrated microfluidic systems with sample preparation and nucleic acid amplification
- PMID: 31365009
- PMCID: PMC8876602
- DOI: 10.1039/c9lc00389d
Integrated microfluidic systems with sample preparation and nucleic acid amplification
Abstract
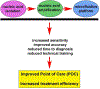
Rapid, efficient and accurate nucleic acid molecule detection is important in the screening of diseases and pathogens, yet remains a limiting factor at point of care (POC) treatment. Microfluidic systems are characterized by fast, integrated, miniaturized features which provide an effective platform for qualitative and quantitative detection of nucleic acid molecules. The nucleic acid detection process mainly includes sample preparation and target molecule amplification. Given the advancements in theoretical research and technological innovations to date, nucleic acid extraction and amplification integrated with microfluidic systems has advanced rapidly. The primary goal of this review is to outline current approaches used for nucleic acid detection in the context of microfluidic systems. The secondary goal is to identify new approaches that will help shape future trends at the intersection of nucleic acid detection and microfluidics, particularly with regard to increasing disease and pathogen detection for improved diagnosis and treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with the current work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prospects of Microfluidic Technology in Nucleic Acid Detection Approaches.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 May 27;13(6):584. doi: 10.3390/bios13060584. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fully integrated microfluidic devices for qualitative, quantitative and digital nucleic acids testing at point of care.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Apr 1;177:112952. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112952. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33453463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated electrochemical microsystems for genetic detection of pathogens at the point of care.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Apr 21;48(4):911-20. doi: 10.1021/ar500456w. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25785632
-
Nucleic acid sample preparation from whole blood in a paper microfluidic device using isotachophoresis.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021 Jan 15;1163:122494. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122494. Epub 2020 Dec 13. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33401049 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Point-of-Care Molecular Diagnostic Devices for Infectious Diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Nov 16;54(22):4107-4119. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00385. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34699183 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetophoresis in Centrifugal Microfluidics at Continuous Rotation for Nucleic Acid Extraction.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Nov 29;13(12):2112. doi: 10.3390/mi13122112. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36557411 Free PMC article.
-
Automated multiplex nucleic acid tests for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2, influenza A and B infection with direct reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (dirRT-qPCR) assay in a centrifugal microfluidic platform.RSC Adv. 2020 Sep 15;10(56):34088-34098. doi: 10.1039/d0ra04507a. eCollection 2020 Sep 10. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35519051 Free PMC article.
-
Visible-light and near-infrared fluorescence and surface-enhanced Raman scattering point-of-care sensing and bio-imaging: a review.Chem Soc Rev. 2022 Jan 4;51(1):329-375. doi: 10.1039/c9cs00621d. Chem Soc Rev. 2022. PMID: 34897302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances and application of whole genome amplification in molecular diagnosis and medicine.MedComm (2020). 2022 Feb 3;3(1):e116. doi: 10.1002/mco2.116. eCollection 2022 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35281794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Powerful CRISPR-Based Biosensing Techniques and Their Integration With Microfluidic Platforms.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 23;10:851712. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.851712. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35284406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

