Rheumatic Fever: A Disease without Color
- PMID: 31365604
- PMCID: PMC6882402
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20190141
Rheumatic Fever: A Disease without Color
Abstract
Background: Brazil has approximately 30.000 cases of Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF) annually. A third of cardiovascular surgeries performed in the country are due to the sequelae of rheumatic heart disease (RHD), which is an important public health problem.
Objectives: to analyze the historical series of mortality rates and disease costs, projecting future trends to offer new data that may justify the need to implement a public health program for RF.
Methods: we performed a cross-sectional study with a time series analysis based on data from the Hospital Information System of Brazil from 1998 to 2016. Simple linear regression models and Holt's Exponential Smoothing Method were used to model the behavior of the series and to do forecasts. The results of the tests with a value of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
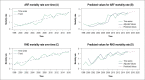
Results: each year, the number of deaths due to RHD increased by an average of 16.94 units and the mortality rate from ARF increased by 215%. There was a 264% increase in hospitalization expenses for RHD and RHD mortality rates increased 42.5% (p-value < 0.05). The estimated mortality rates for ARF and RHD were, respectively, 2.68 and 8.53 for 2019. The estimated cost for RHD in 2019 was US$ 26.715.897,70.
Conclusions: according to the Brazilian reality, the 1-year RHD expenses would be sufficient for secondary prophylaxis (considering a Benzatin Penicillin G dose every 3 weeks) in 22.574 people for 10 years. This study corroborates the need for public health policies aimed at RHD.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




Comment in
-
Rheumatic Fever in Brazil: What Color Should It Be?Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019 Oct 10;113(3):355-356. doi: 10.5935/abc.20190178. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31621774 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Braga ALL, Achutti AC, Ramos AIO, Weksler C, Mota CCC, Santos CCL, et al. Diretrizes Brasileiras para o Diagnóstico, Tratamento e Prevenção da Febre Reumática. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2009;93(3 Suppl 4):1–18. - PubMed
-
- Veasy LG, Tani LY, Daly JA, Korgenski K, Miner L, Bale J, et al. Temporal association of the appearance of mucoid strains of Streptococcus pyogenes with a continuing high incidence of rheumatic fever in Utah. Pt 1Pediatrics. 2004;113(3):e168–e172. - PubMed
-
- Bisno AL, Gerber MA, Gwaltney JM, Kaplan EL, Schwartz RH, Infectious Diseases Society of America Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35(2):113–125. - PubMed
-
- WHO Rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2004;923:1–122. - PubMed
-
- Moran M, Guzman J, Abela-Oversteigen L, Liyanage R, Omune B, Wu L, et al. Neglected disease research and development?: is innovation under threat?? Policy Cures. 2011
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

