Brazilian multicenter study on pegvisomant treatment in acromegaly
- PMID: 31365632
- PMCID: PMC10528655
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000159
Brazilian multicenter study on pegvisomant treatment in acromegaly
Abstract
Objective: Investigate the therapeutic response of acromegaly patients to pegvisomant (PEGV) in a real-life, Brazilian multicenter study.
Subjects and methods: Characteristics of acromegaly patients treated with PEGV were reviewed at diagnosis, just before and during treatment. All patients with at least two IGF-I measurements on PEGV were included. Efficacy was defined as any normal IGF-I measurement during treatment. Safety data were reviewed. Predictors of response were determined by comparing controlled versus uncontrolled patients.
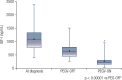
Results: 109 patients [61 women; median age at diagnosis 34 years; 95.3% macroadenomas] from 10 Brazilian centers were studied. Previous treatment included surgery (89%), radiotherapy (34%), somatostatin receptor ligands (99%), and cabergoline (67%). Before PEGV, median levels of GH, IGF-I and IGF-I % of upper limit of normal were 4.3 µg/L, 613 ng/mL, and 209%, respectively. Pre-diabetes/diabetes was present in 48.6% and tumor remnant in 71% of patients. Initial dose was 10 mg/day in all except 4 cases, maximum dose was 30 mg/day, and median exposure time was 30.5 months. PEGV was used as monotherapy in 11% of cases. Normal IGF-I levels was obtained in 74.1% of patients. Glycemic control improved in 56.6% of patients with pre-diabetes/diabetes. Exposure time, pre-treatment GH and IGF-I levels were predictors of response. Tumor enlargement occurred in 6.5% and elevation of liver enzymes in 9.2%. PEGV was discontinued in 6 patients and 3 deaths unrelated to the drug were reported.
Conclusions: In a real-life scenario, PEGV is a highly effective and safe treatment for acromegaly patients not controlled with other therapies.
Figures

Comment in
-
Pegvisomant for acromegaly: does it always works?Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Aug 22;63(4):318-319. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000163. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31460621 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- de Vos AM, Ultsch M, Kossiakoff AA. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992;255(5042):306-12. - PubMed
-
- Brooks AJ, Dai W, O’Mara ML, Abankwa D, Chhabra Y, Pelekanos RA, et al. Mechanism of activation of protein kinase JAK2 by the growth hormone receptor. Science. 2014;344(6185):1249783. - PubMed
-
- Kopchick JJ, Parkinson C, Stevens EC, Trainer PJ. Growth hormone receptor antagonists: discovery, development, and use in patients with acromegaly. Endocr Rev. 2002;23(5):623-46. - PubMed
-
- Tritos NA, Biller BM. Pegvisomant: a growth hormone receptor antagonist used in the treatment of acromegaly. Pituitary. 2017;20(1):129-35. - PubMed
-
- Melmed S. New therapeutic agents for acromegaly. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(2):90-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
