Pemphigus vulgaris
- PMID: 31365654
- PMCID: PMC6668932
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20199011
Pemphigus vulgaris
Abstract
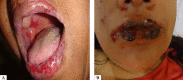
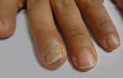
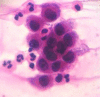
Pemphigus vulgaris is a chronic autoimmune bullous dermatosis that results from the production of autoantibodies against desmogleins 1 and 3. It is the most frequent and most severe form of pemphigus, occurring universally, usually between 40 and 60 years of age. It usually begins with blisters and erosions on the oral mucosa, followed by lesions on other mucous membranes and flaccid blisters on the skin, which can be disseminated. There is a clinical variant, pemphigus vegetans, which is characterized by the presence of vegetating lesions in the large folds of the skin. Clinical suspicion can be confirmed by cytological examination, histopathological examination, and direct and indirect immunofluorescence tests. The treatment is performed with systemic corticosteroids, and immunosuppressive drugs may be associated, among them azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil. More severe cases may benefit from corticosteroids in the form of intravenous pulse therapy, and recent studies have shown a beneficial effect of rituximab, an anti-CD20 immunobiological drug. It is a chronic disease with mortality around 10%, and septicemia is the main cause of death. Patients need long-term and multidisciplinary follow-up.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures







References
-
- Kridin K, Sagi SZ, Bergman R. Mortality and cause of death in Israeli patients with pemphigus. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:607–611. - PubMed
-
- Hsu DY, Brieva J, Sinha AA, Langan SM, Silverberg J. Comorbidities and inpatient mortality for pemphigus in the USA. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:1290–1298. - PubMed
-
- Di Zenzo G, Amber KT, Sayar BS, Müller EJ, Borradori L. Immune response in pemphigus and beyond: progresses and emerging concepts. Semin Immunopathol. 2016;38:57–74. - PubMed
-
- Pan M, Liu X, Zheng J. The pathogenic role of autoantibodies in pemphigus vulgaris. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:703–707. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

