Treatment of actinic keratoses and cancerization field of the face and scalp with 0.015% ingenol mebutate gel in Brazilian individuals: safety, tolerability and patients' perspectives
- PMID: 31365660
- PMCID: PMC6668952
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20197938
Treatment of actinic keratoses and cancerization field of the face and scalp with 0.015% ingenol mebutate gel in Brazilian individuals: safety, tolerability and patients' perspectives
Abstract
Background: Actinic keratosis (AK) represents a risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Ingenol mebutate gel is a novel therapeutic option for field-directed treatment.
Objectives: To evaluate the safety, tolerability and patients' perspectives, related to the therapeutic success of managing AKs on the face and scalp with ingenol mebutate gel in Brazilian individuals.
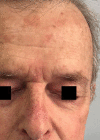
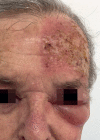
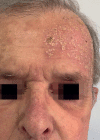
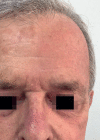
Methods: This was an observational, retrospective and descriptive study of 68 areas of actinic keratosis on the face and scalp treated with Ingenol mebutate gel involving a total of 37 patients. The drug was applied for three consecutive days on an area of of 25 cm2 and documentation was performed on baseline and days 4, 8, 15, 60 and 180. On day 4, the composite local skin reaction score was calculated. At the end, a questionnaire was applied to evaluate patients' perspectives about the treatment.
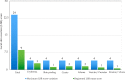
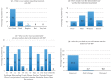
Results: Adherence was 100%, no serious adverse events were recorded and the mean composite local skin reaction score (standard deviation) was 8.61±4.22. The treatment was considered optimum by 75.68% of the patients.
Study limitations: Calculation of composite local skin reaction score performed only on the fourth day.
Conclusions: Treatment with ingenol mebutate gel was considered safe and tolerable in Brazilian subjects. Patients had a maximum adherence rate and a great improvement in self-esteem. The results of this research reproduce the findings of the literature.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Three of the authors received honorarium from LEO Pharma. One as a speaker (Luiz Alberto Gameiro Jr) and the other two as Board consultants (Luís Fernando Requejo Tovo e José Antonio Sanches Jr).
Figures
References
-
- Einspahr JG, Stratton SP, Bowden GT, Alberts DS. Chemoprevention of human skin cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2002;41:269–285. - PubMed
-
- Vatve M, Ortonne JP, Birch-Machin MA, Gupta G. Management of field change in actinic keratosis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(Suppl 2):21–24. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt JV, Miot HA. Queratoses actínicas: revisão clínica e epidemiológica. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Landis ET, Davis SA, Taheri A, Feldman SR. Top dermatologic diagnoses by age. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:22368. - PubMed
-
- Sociedade Brasileira de Dermatologia Nosologic profile of dermatologic visits in Brazil. An Bras Dermatol. 2006;81:549–558.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

