Secretome of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs) as a Novel Trend in Chronic Non-Healing Wounds: An Overview of Experimental In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and Methodological Variables
- PMID: 31366040
- PMCID: PMC6696601
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20153721
Secretome of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs) as a Novel Trend in Chronic Non-Healing Wounds: An Overview of Experimental In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and Methodological Variables
Abstract
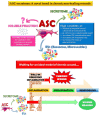
Wound healing is a complex process with a linear development that involves many actors in a multistep timeline commonly divided into four stages: Hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Chronic non-healing wounds fail to progress beyond the inflammatory phase, thus precluding the next steps and, ultimately, wound repair. Many intrinsic or extrinsic factors may contribute to such an occurrence, including patient health conditions, age-related diseases, metabolic deficiencies, advanced age, mechanical pressure, and infections. Great interest is being focused on the adipose tissue-derived stem cell's (ASC) paracrine activity for its potential therapeutic impact on chronic non-healing wounds. In this review, we summarize the results of in vitro and in vivo experimental studies on the pro-wound healing effects of ASC-secretome and/or extracellular vesicles (EVs). To define an overall picture of the available literature data, experimental conditions and applied methodologies are described as well as the in vitro and in vivo models chosen in the reported studies. Even if a comparative analysis of the results obtained by the different groups is challenging due to the large variability of experimental conditions, the available findings are undoubtedly encouraging and fully support the use of cell-free therapies for the treatment of chronic non-healing wounds.
Keywords: adipose tissue-derived stem cells; chronic non-healing wounds; experimental models; secretome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nussbaum S.R., Carter M.J., Fife C.E., DaVanzo J., Haught R., Nusgart M., Cartwright D. An economic evaluation of the impact, cost, and medicare policy implications of chronic nonhealing wounds. Value Health J. Int. Soc. Pharm. Outcomes Res. 2018;21:27–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2017.07.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

