Wild Nutria (Myocastor coypus) Is a Potential Reservoir of Carbapenem-Resistant and Zoonotic Aeromonas spp. in Korea
- PMID: 31366125
- PMCID: PMC6723217
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms7080224
Wild Nutria (Myocastor coypus) Is a Potential Reservoir of Carbapenem-Resistant and Zoonotic Aeromonas spp. in Korea
Abstract
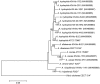
The emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant Aeromonas spp. is a serious public and animal health concern. Wild animals serve as reservoirs, vectors, and sentinels of these bacteria and can facilitate their transmission to humans and livestock. The nutria (Myocastor coypus), a semi-aquatic rodent, currently is globally considered an invasive alien species that has harmful impacts on natural ecosystems and carries various zoonotic aquatic pathogens. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant zoonotic Aeromonas spp. in wild invasive nutrias captured in Korea during governmental eradication program. Three potential zoonotic Aeromonas spp. (A. hydrophila, A. caviae, and A. dhakensis) were identified among isolates from nutria. Some strains showed unexpected resistance to fluoroquinolones, third-generation cephalosporins, and carbapenems. In carbapenem-resistant isolates, the cphA gene, which is related to intrinsic resistance of Aeromonas to carbapenems, was identified, and phylogenetic analysis based on this gene revealed the presence of two major groups represented by A. hydrophila (including A. dhakensis) and other Aeromonas spp. These results indicate that wild nutrias in Korea are a potential reservoir of zoonotic and antibiotic-resistant Aeromonas spp. that can cause infection and treatment failure in humans. Thus, measures to prevent contact of wild nutrias with livestock and humans are needed.
Keywords: Aeromonas spp.; antibiotic resistance; carbapenem; cphA; nutria (Myocastor coypus).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complete Genome Sequence of Aeromonas rivipollensis KN-Mc-11N1, Isolated from a Wild Nutria (Myocastor coypus) in South Korea.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018 Aug 2;7(4):e00907-18. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00907-18. eCollection 2018 Aug. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018. PMID: 30533878 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Nutria (Myocastor coypus) in South Korea.Animals (Basel). 2019 Dec 17;9(12):1164. doi: 10.3390/ani9121164. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31861229 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Third Generation Cephalosporin- and Carbapenem-Resistant Aeromonas Isolates from Municipal and Hospital Wastewater.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;12(3):513. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030513. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978380 Free PMC article.
-
A review of productive parameters, nutritive value and technological characteristics of farmed nutria meat (Myocastor coypus).Meat Sci. 2019 Feb;148:137-149. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Meat Sci. 2019. PMID: 30388478 Review.
-
Aeromonas dhakensis, an Increasingly Recognized Human Pathogen.Front Microbiol. 2016 May 27;7:793. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00793. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27303382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low potential of persistence and dissemination of antimicrobial-resistant Enterobacterales by wild nutria (Myocastor coypus) in a local river of Gifu Prefecture.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 Jun 1;85(6):613-616. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0042. Epub 2023 May 2. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37150602 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic, molecular detection and antibiogram analysis of Aeromonas Hydrophila from Oreochromis Niloticus (Nile Tilapia) and Ready-To- eat fish products in selected Rift Valley lakes of Ethiopia.BMC Vet Res. 2023 Aug 12;19(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03684-3. BMC Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37573362 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Epidemiology, Virulence Traits and Antimicrobial Resistance Signatures of Aeromonas spp. in the Critically Endangered Iberochondrostoma lusitanicum Follow Geographical and Seasonal Patterns.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 22;10(7):759. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070759. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206643 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of Myocastor coypus Infected with Staphylococcus cohnii.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2024 Mar 27;2024:3710299. doi: 10.1155/2024/3710299. eCollection 2024. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2024. PMID: 40303031 Free PMC article.
-
Zoonotic Agents in Farmed Fish: A Systematic Review from the Interdisciplinary Perspective of the One Health Concept.Vet Sci. 2025 May 2;12(5):437. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050437. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Colwell R.R., MacDonell M.T., De Ley J. Proposal to recognize the family Aeromonadaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1986;36:473–477. doi: 10.1099/00207713-36-3-473. - DOI
-
- Khajanchi B.K., Fadl A.A., Borchardt M.A., Berg R.L., Horneman A.J., Stemper M.E., Joseph S.W., Moyer N.P., Sha J., Chopra A.K. Distribution of virulence factors and molecular fingerprinting of Aeromonas species isolates from water and clinical samples: suggestive evidence of water-to-human transmission. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;76:2313–2325. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02535-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

