The androgen receptor regulates a druggable translational regulon in advanced prostate cancer
- PMID: 31366581
- PMCID: PMC6746573
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw4993
The androgen receptor regulates a druggable translational regulon in advanced prostate cancer
Abstract
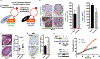
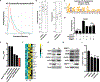
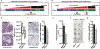
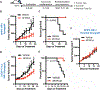
The androgen receptor (AR) is a driver of cellular differentiation and prostate cancer development. An extensive body of work has linked these normal and aberrant cellular processes to mRNA transcription; however, the extent to which AR regulates posttranscriptional gene regulation remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that AR uses the translation machinery to shape the cellular proteome. We show that AR is a negative regulator of protein synthesis and identify an unexpected relationship between AR and the process of translation initiation in vivo. This is mediated through direct transcriptional control of the translation inhibitor 4EBP1. We demonstrate that lowering AR abundance increases the assembly of the eIF4F translation initiation complex, which drives enhanced tumor cell proliferation. Furthermore, we uncover a network of pro-proliferation mRNAs characterized by a guanine-rich cis-regulatory element that is particularly sensitive to eIF4F hyperactivity. Using both genetic and pharmacologic methods, we demonstrate that dissociation of the eIF4F complex reverses the proliferation program, resulting in decreased tumor growth and improved survival in preclinical models. Our findings reveal a druggable nexus that functionally links the processes of mRNA transcription and translation initiation in an emerging class of lethal AR-deficient prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures


Comment in
-
AR - the link between transcription and translation.Nat Rev Urol. 2019 Oct;16(10):565. doi: 10.1038/s41585-019-0229-8. Nat Rev Urol. 2019. PMID: 31455866 No abstract available.
-
Re: The Androgen Receptor Regulates a Druggable Translational Regulon in Advanced Prostate Cancer.J Urol. 2020 Mar;203(3):466. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000679.01. Epub 2019 Dec 3. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31793808 No abstract available.
-
Towards understanding androgen receptor-independent prostate cancer: an evolving paradigm.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(2):415-417. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.01.25. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117385 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protein translation controlled by the androgen receptor in prostate cancer: a novel therapeutic option?Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Apr;9(4):2171-2174. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.02.31. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117576 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dehm SM, Tindall DJ, Androgen receptor structural and functional elements: role and regulation in prostate cancer. Mol Endocrinol 21, 2855–2863 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hsieh AC, Small EJ, Ryan CJ, Androgen-response elements in hormone-refractory prostate cancer: implications for treatment development. Lancet Oncol 8, 933–939 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Schwanhausser B, Busse D, Li N, Dittmar G, Schuchhardt J, Wolf J, Chen W, Selbach M, Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473, 337–342 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F30 CA224951/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097186/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003324/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P50 CA092629/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000585/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P01 CA163227/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK106829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA182503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA193837/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA208100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009515/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020069/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA224079/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007266/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA230617/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA224044/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

