A comprehensive study on genome-wide coexpression network of KHDRBS1/Sam68 reveals its cancer and patient-specific association
- PMID: 31366900
- PMCID: PMC6668649
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-47558-x
A comprehensive study on genome-wide coexpression network of KHDRBS1/Sam68 reveals its cancer and patient-specific association
Abstract
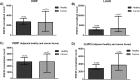
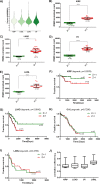
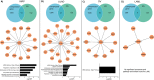
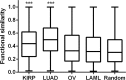
Human KHDRBS1/Sam68 is an oncogenic splicing factor involved in signal transduction and pre-mRNA splicing. We explored the molecular mechanism of KHDRBS1 to be a prognostic marker in four different cancers. Within specific cancer, including kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma (KIRP), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), acute myeloid leukemia (LAML), and ovarian cancer (OV), KHDRBS1 expression is heterogeneous and patient specific. In KIRP and LUAD, higher expression of KHDRBS1 affects the patient survival, but not in LAML and OV. Genome-wide coexpression analysis reveals genes and transcripts which are coexpressed with KHDRBS1 in KIRP and LUAD, form the functional modules which are majorly involved in cancer-specific events. However, in case of LAML and OV, such modules are absent. Irrespective of the higher expression of KHDRBS1, the significant divergence of its biological roles and prognostic value is due to its cancer-specific interaction partners and correlation networks. We conclude that rewiring of KHDRBS1 interactions in cancer is directly associated with patient prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sam68/KHDRBS1 is critical for colon tumorigenesis by regulating genotoxic stress-induced NF-κB activation.Elife. 2016 Jul 25;5:e15018. doi: 10.7554/eLife.15018. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27458801 Free PMC article.
-
c-MYC empowers transcription and productive splicing of the oncogenic splicing factor Sam68 in cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):6160-6171. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz344. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31066450 Free PMC article.
-
KHDRBS1 as a novel prognostic signaling biomarker influencing hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, immune microenvironment, and drug sensitivity.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 10;15:1393801. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1393801. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38660302 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sam68 in different types of cancer (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jan;55(1):3. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5444. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39450529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the RNA-binding protein Sam68 as a treatment for cancer?Future Oncol. 2007 Oct;3(5):539-44. doi: 10.2217/14796694.3.5.539. Future Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17927519 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Shotgun Proteomics Reveals the Characteristic Protein Signature of Osteosarcoma Subtypes.Cells. 2023 Aug 30;12(17):2179. doi: 10.3390/cells12172179. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681913 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine Receptors and TAAR1 Functional Interaction Patterns in the Duodenum Are Impaired in Gastrointestinal Disorders.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 17;12(7):1590. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071590. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062162 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of Sam68 contributes to metastasis by regulating vimentin expression and a motile phenotype in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2022 Oct;48(4):183. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8398. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36082807 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory roles and mechanisms of alternative RNA splicing in adipogenesis and human metabolic health.Cell Biosci. 2021 Apr 1;11(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00581-w. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33795017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Game-theoretic link relevance indexing on genome-wide expression dataset identifies putative salient genes with potential etiological and diapeutics role in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 4;12(1):13409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17266-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35927308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lukong KE, Richard S. Sam68, the KH domain-containing superSTAR. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2003;1653:73–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

