The resurgence of estrogens in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 31367069
- PMCID: PMC6639989
- DOI: 10.4103/iju.IJU_56_19
The resurgence of estrogens in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
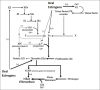
Use of exogenous estrogens in manipulating the androgenestrogen equilibrium was one of the earliest therapeutic strategies developed to treat prostate cancer which followed close on heels the discovery of hormone dependence of this tumor. Despite its well-documented benefit, estrogen therapy fell out of favor with the advent of other forms of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) as the former registered a higher incidence of cardiovascular complications and poorer overall survival. Clearer understanding of the mechanism of action of estrogen coupled with the adoption of alternative routes of administration has triggered a renewed interest in estrogen therapy. Since then, many studies have not only proved the therapeutic benefit of estrogens but also explored the ways and means of minimizing the dreaded side effects deterring its use. Further, the fact that estrogen therapy offered a clear advantage of reduced cost of treatment over other treatments has led many countries to readopt it in the treatment of advanced prostatic cancer. We reviewed the published data on the use of estrogens in CRPC, which may affect its revival as an efficacious treatment option having minimal side effects, with modified dosage and route of administration. Estrogen therapy would be a less expensive option having equivalent or even better therapeutic effect than ADT in advanced carcinoma of prostate.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Santti R, Newbold RR, Mäkelä S, Pylkkänen L, McLachlan JA. Developmental estrogenization and prostatic neoplasia. Prostate. 1994;24:67–78. - PubMed
-
- Thomas JA, Keenan EJ. Effects of estrogens on the prostate. J Androl. 1994;15:97–9. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen PL, Alibhai SM, Basaria S, D'Amico AV, Kantoff PW, Keating NL, et al. Adverse effects of androgen deprivation therapy and strategies to mitigate them. Eur Urol. 2015;67:825–36. - PubMed
-
- Barrett-Connor E, Garland C, McPhillips JB, Khaw KT, Wingard DL. A prospective, population-based study of androstenedione, estrogens, and prostatic cancer. Cancer Res. 1990;50:169–73. - PubMed
-
- Modugno F, Weissfeld JL, Trump DL, Zmuda JM, Shea P, Cauley JA, et al. Allelic variants of aromatase and the androgen and estrogen receptors: Toward a multigenic model of prostate cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3092–6. - PubMed