Diagnostic accuracy of intermediate b-value diffusion-weighted imaging for detection of residual hepatocellular carcinoma following transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads
- PMID: 31367092
- PMCID: PMC6639864
- DOI: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_383_18
Diagnostic accuracy of intermediate b-value diffusion-weighted imaging for detection of residual hepatocellular carcinoma following transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the role of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) in the detection of residual malignant tumor of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) with drug-eluting beads (DEBs).
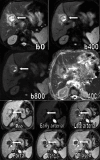
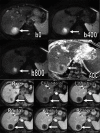
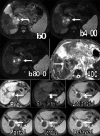
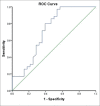
Subjects and methods: Pre-contrast T1, T2, dynamic contrast-enhanced, and respiratory-triggered DW-MRI (b factor 0, 400, and 800 s/mm2) were obtained in 60 patients with HCC who underwent tran-sarterial hepatic chemoembolization with DEBs. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated for the DW imaging images. Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) were calculated searching for the optimal cut-off value using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results: DW-MRI had a sensitivity of 77.1%, a specificity of 60.7%, a PPV of 71.05%, and a NPV of 68%. The difference between the malignant and benign groups' ADC variables was statistically significant (P < 0.003). The ROC curve showed that the area under the curve is C = 0.718 with SE = 0.069 and 95% confidence interval from 0.548 to 0.852.
Conclusion: In our study, we demonstrated that diffusion MRI has limited diagnostic value in the assessment of viable tumor tissue after TACE with DEBs in cases of HCC.
Keywords: Drug-eluting beads; diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging; hepatic; hepatocellular carcinoma-transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; malignant.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as a Noninvasive Biomarker for the Early Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Using Drug-eluting Beads.Curr Med Imaging. 2022;18(11):1186-1194. doi: 10.2174/1573405618666220304141632. Curr Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35249499
-
Value of Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Detecting Residual Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Drug-Eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization.Acad Radiol. 2021 Jun;28(6):790-798. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 May 13. Acad Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32414638
-
Immediate post-doxorubicin drug-eluting beads chemoembolization Mr Apparent diffusion coefficient quantification predicts response in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Oct;42(4):981-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24845. Epub 2015 Feb 12. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25683022 Clinical Trial.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization using drug eluting beads for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Now and future.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015 Dec;21(4):344-8. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2015.21.4.344. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26770921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging for Assessing the Therapeutic Response of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 Feb 10;11(8):2339-2347. doi: 10.7150/jca.32491. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32127960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Utility of diffusion weighted imaging with the quantitative apparent diffusion coefficient in diagnosing residual or recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization: a meta-analysis.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Jan 6;20(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40644-019-0282-9. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31907050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corona-Villalobos CP, Halappa VG, Geschwind JF, Bonekamp S, Reyes D, Cosgrove D, et al. Volumetric assessment of tumor response using functional MR imaging in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with a combination of doxorubicin-eluting beads and sorafenib. Eur Radiol. 2015;25:380–90. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Özkavukcu E, Haliloǧlu N, Erden A. Post-treatment MRI findings of hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009;15:111–20. - PubMed
-
- Kamel IR, Morgan HR. MRI appearance of treated liver lesions. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2011;19
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

