A comparison of ultra-high-resolution CT target scan versus conventional CT target reconstruction in the evaluation of ground-glass-nodule-like lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31367562
- PMCID: PMC6629564
- DOI: 10.21037/qims.2019.06.09
A comparison of ultra-high-resolution CT target scan versus conventional CT target reconstruction in the evaluation of ground-glass-nodule-like lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to determine whether the clinical value of scanned computed tomography (CT) images is higher when using ultra-high-resolution CT (U-HRCT) target scanning than conventional CT target reconstruction scanning in the evaluation of ground-glass-nodule (GGN)-like lung adenocarcinoma.
Methods: A total of 91 consecutive patients with isolated GGN-like lung adenocarcinoma were included in this study from April 2017 to June 2018. U-HRCT and conventional CT scans were conducted in all enrolled patients. Two experienced thoracic radiologists independently assessed image quality and made diagnoses. Based on the pathological results, the accuracies of U-HRCT target scanning and conventional CT target reconstruction for detecting morphological features on CT, including spiculation of GGNs, bronchial vascular bundles, solid components in the nodules, burr, vacuole, air bronchial signs, and fissure distortion, were calculated. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 17.0 software. Enumeration data were tested using the Chi-square test. A P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
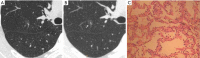
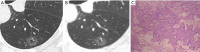
Results: When both techniques were compared with the pathological findings, the detection rate for CT images obtained using U-HRCT target scanning and conventional CT target reconstruction with regard to the spiculation of GGNs, bronchial vascular bundles, and solid components in the nodules were 78% vs. 61.5%, 72.5% vs. 54.9%, 65.9% vs. 49.5%, respectively. The presence of the spiculation of GGNs, bronchial vascular bundles, and solid components in the nodules in U-HRCT target scanning was significantly higher than that in conventional CT target reconstruction (all P<0.05). However, no significant difference was observed between the two techniques with regard to the burr, vacuole, air bronchial signs, and fissure distortion (all P>0.05).
Conclusions: When viewing GGNs, the detection rate was higher for U-HRCT target scanning than for conventional CT target reconstruction, and this improvement significantly enhanced the diagnostic accuracy of early lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: Ultra-high-resolution CT target scan (U-HRCT target scan); conventional CT target reconstruction; ground-glass opacity; lung adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Todo G, Ito H, Nakano Y, Dodo Y, Maeda H, Murata K, Odori T, Torizuka K, Izumi T, Oshima S. High resolution CT (HR-CT) for the evaluation of pulmonary peripheral disorders. Rinsho Hoshasen 1982;27:1319-26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
