Missense mutations in the C-terminal portion of the B4GALNT2-encoded glycosyltransferase underlying the Sd(a-) phenotype
- PMID: 31367682
- PMCID: PMC6646742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.100659
Missense mutations in the C-terminal portion of the B4GALNT2-encoded glycosyltransferase underlying the Sd(a-) phenotype
Abstract
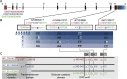
Sda is a high-frequency carbohydrate histo-blood group antigen, GalNAcβ1-4(NeuAcα2-3)Galβ, implicated in pathogen invasion, cancer, xenotransplantation and transfusion medicine. Complete lack of this glycan epitope results in the Sd(a-) phenotype observed in 4% of individuals who may produce anti-Sda. A candidate gene (B4GALNT2), encoding a Sda-synthesizing β-1,4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (β4GalNAc-T2), was cloned in 2003 but the genetic basis of human Sda deficiency was never elucidated. Experimental and bioinformatic approaches were used to identify and characterize B4GALNT2 variants in nine Sd(a-) individuals. Homozygosity for rs7224888:T > C dominated the cohort (n = 6) and causes p.Cys466Arg, which targets a highly conserved residue located in the enzymatically active domain and is judged deleterious to β4GalNAc-T2. Its allele frequency was 0.10-0.12 in different cohorts. A Sd(a-) compound heterozygote combined rs7224888:T > C with a splice-site mutation, rs72835417:G > A, predicted to alter splicing and occurred at a frequency of 0.11-0.12. Another compound heterozygote had two rare nonsynonymous variants, rs148441237:A > G (p.Gln436Arg) and rs61743617:C > T (p.Arg523Trp), in trans. One sample displayed no differences compared to Sd(a+). When investigating linkage disequilibrium between B4GALNT2 variants, we noted a 32-kb block spanning intron 9 to the intergenic region downstream of B4GALNT2. This block includes RP11-708H21.4, a long non-coding RNA recently reported to promote tumorigenesis and poor prognosis in colon cancer. The expression patterns of B4GALNT2 and RP11-708H21.4 correlated extremely well in >1000 cancer cell lines. In summary, we identified a connection between variants of the cancer-associated B4GALNT2 gene and Sda, thereby establishing a new blood group system and opening up for the possibility to predict Sd(a+) and Sd(a‒) phenotypes by genotyping.
Keywords: B4GALNT2; Glycosyltransferase; Red blood cell; Sd(a‒) phenotype; Sda histo-blood group antigen.
Figures



References
-
- Renton P.H., Howell P., Ikin E.W. Anti-Sda, a new blood group antibody. Vox Sang. 1967;13:493–501.
-
- Macvie S.I., Morton J.A., Pickles M.M. The reactions and inheritance of a new blood group antigen, Sda. Vox Sang. 1967;13:485–492.
-
- Reid M.E., Lomas-Francis C., Olsson M.L. third ed. Academic Press; London, UK: 2012. The Blood Group Antigen FactsBook.
-
- Morton J.A., Pickles M.M., Terry A.M. The Sda blood group antigen in tissues and body fluids. Vox Sang. 1970;19:472–482. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

