The quantitative neuroradiology initiative framework: application to dementia
- PMID: 31368776
- PMCID: PMC6732931
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20190365
The quantitative neuroradiology initiative framework: application to dementia
Abstract
There are numerous challenges to identifying, developing and implementing quantitative techniques for use in clinical radiology, suggesting the need for a common translational pathway. We developed the quantitative neuroradiology initiative (QNI), as a model framework for the technical and clinical validation necessary to embed automated segmentation and other image quantification software into the clinical neuroradiology workflow. We hypothesize that quantification will support reporters with clinically relevant measures contextualized with normative data, increase the precision of longitudinal comparisons, and generate more consistent reporting across levels of radiologists' experience. The QNI framework comprises the following steps: (1) establishing an area of clinical need and identifying the appropriate proven imaging biomarker(s) for the disease in question; (2) developing a method for automated analysis of these biomarkers, by designing an algorithm and compiling reference data; (3) communicating the results via an intuitive and accessible quantitative report; (4) technically and clinically validating the proposed tool pre-use; (5) integrating the developed analysis pipeline into the clinical reporting workflow; and (6) performing in-use evaluation. We will use current radiology practice in dementia as an example, where radiologists have established visual rating scales to describe the degree and pattern of atrophy they detect. These can be helpful, but are somewhat subjective and coarse classifiers, suffering from floor and ceiling limitations. Meanwhile, several imaging biomarkers relevant to dementia diagnosis and management have been proposed in the literature; some clinically approved radiology software tools exist but in general, these have not undergone rigorous clinical validation in high volume or in tertiary dementia centres. The QNI framework aims to address this need. Quantitative image analysis is developing apace within the research domain. Translating quantitative techniques into the clinical setting presents significant challenges, which must be addressed to meet the increasing demand for accurate, timely and impactful clinical imaging services.
Figures

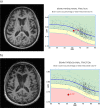
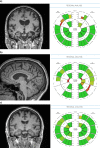
References
-
- Bosco P, Redolfi A, Bocchetta M, Ferrari C, Mega A, Galluzzi S, et al. . The impact of automated hippocampal volumetry on diagnostic confidence in patients with suspected Alzheimer's disease: a European Alzheimer's disease Consortium study. Alzheimers Dement 2017; 13: 1013–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.01.019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- REGULATION (EU) 2017/745 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 5 April 2017 on medical Devices, amending Directive 2001/83/EC, regulation (EC) NO 178/2002 and regulation (EC) NO 1223/2009 and repealing Council directives 90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC. Off J Eur Union 2017: 60.
-
- Clarke LP, Sriram RD, Schilling LB. Imaging as a biomarker: standards for change measurements in therapy workshop summary. Acad Radiol 2008; 15: 501–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

