Diagnostic performance of a single and duplicate Kato-Katz, Mini-FLOTAC, FECPAKG2 and qPCR for the detection and quantification of soil-transmitted helminths in three endemic countries
- PMID: 31369558
- PMCID: PMC6675048
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007446
Diagnostic performance of a single and duplicate Kato-Katz, Mini-FLOTAC, FECPAKG2 and qPCR for the detection and quantification of soil-transmitted helminths in three endemic countries
Abstract
Background: Because the success of deworming programs targeting soil-transmitted helminths (STHs) is evaluated through the periodically assessment of prevalence and infection intensities, the use of the correct diagnostic method is of utmost importance. The STH community has recently published for each phase of a deworming program the minimal criteria that a potential diagnostic method needs to meet, the so-called target product profiles (TPPs).
Methodology: We compared the diagnostic performance of a single Kato-Katz (reference method) with that of other microscopy-based methods (duplicate Kato-Katz, Mini-FLOTAC and FECPAKG2) and one DNA-based method (qPCR) for the detection and quantification of STH infections in three drug efficacy trials in Ethiopia, Lao PDR, and Tanzania. Furthermore, we evaluated a selection of minimal diagnostic criteria of the TPPs.
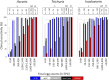
Principal findings: All diagnostic methods showed a clinical sensitivity of ≥90% for all STH infections of moderate-to-heavy intensities. For infections of very low intensity, only qPCR resulted in a sensitivity that was superior to a single Kato-Katz for all STHs. Compared to the reference method, both Mini-FLOTAC and FECPAKG2 resulted in significantly lower fecal egg counts for some STHs, leading to a substantial underestimation of the infection intensity. For qPCR, there was a positive significant correlation between the egg counts of a single Kato-Katz and the DNA concentration.
Conclusions/significance: Our results indicate that the diagnostic performance of a single Kato-Katz is underestimated by the community and that diagnostic specific thresholds to classify intensity of infection are warranted for Mini-FLOTAC, FECPAKG2 and qPCR. When we strictly apply the TPPs, Kato-Katz is the only microscopy-based method that meets the minimal diagnostic criteria for application in the planning, monitoring and evaluation phase of an STH program. qPCR is the only method that could be considered in the phase that aims to seek confirmation for cessation of program.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03465488.
Conflict of interest statement
The FECPAKG2 technology was produced and distributed by Techion Group Ltd, of which ET is an employee and GM is managing director. Both hold stocks in Techion Group Ltd. The Mini-FLOTAC device is a commercial product distributed by GC, LR and MPM through the University of Napoli Federico II. However, the affiliations of ET, GM, GC, LR and MPM did not play any role in the preparation and submission of this manuscript. All other authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Hay S, Abajobir A, Abate K, Abbafati C, Abbas K, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1260–344. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32130-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Preventive chemotherapy to control soil-transmitted helminth infections in at-risk population groups. Geneva, 2017. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Soil-transmitted helminthiasis—eliminating soil-transmitted helminthiases as a public health problem in children Soil-transmittted helminthiases progress report 2001–2010 and strategic plan 2011–2020. Geneva, 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

