Zebrafish Exploit Visual Cues and Geometric Relationships to Form a Spatial Memory
- PMID: 31369985
- PMCID: PMC6669324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.07.013
Zebrafish Exploit Visual Cues and Geometric Relationships to Form a Spatial Memory
Abstract
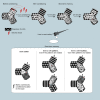
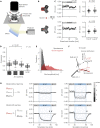
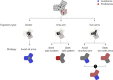
Animals use salient cues to navigate in their environment, but their specific cognitive strategies are largely unknown. We developed a conditioned place avoidance paradigm to discover whether and how zebrafish form spatial memories. In less than an hour, juvenile zebrafish, as young as 3 weeks, learned to avoid the arm of a Y-maze that was cued with a mild electric shock. Interestingly, individual fish solved this task in different ways: by staying in the safe center of the maze or by preference for one, or both, of the safe arms. In experiments in which the learned patterns were swapped, rotated, or replaced, the animals could transfer the association of safety to a different arm or to a different pattern using either visual cues or location as the conditioned stimulus. These findings show that juvenile zebrafish exhibit several complementary spatial learning modes, which generate a flexible repertoire of behavioral strategies.
Keywords: Behavioral Neuroscience; Biological Sciences; Evolutionary Biology.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Parallel processing of information about location in the amygdala, entorhinal cortex and hippocampus.Hippocampus. 2013 Nov;23(11):1075-83. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22179. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23929819 Review.
-
Place versus response learning in fish: a comparison between species.Anim Cogn. 2016 Jan;19(1):153-61. doi: 10.1007/s10071-015-0922-9. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Anim Cogn. 2016. PMID: 26385107
-
Y-maze avoidance: an automated and rapid associative learning paradigm in zebrafish.Neurosci Res. 2015 Feb;91:69-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Neurosci Res. 2015. PMID: 25449146
-
Acute stress disrupts performance of zebrafish in the cued and spatial memory tests: the utility of fish models to study stress-memory interplay.Behav Processes. 2011 Jun;87(2):224-30. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2011.04.004. Epub 2011 May 3. Behav Processes. 2011. PMID: 21545830
-
Evolutionary conservation, translational relevance and cognitive function: The future of zebrafish in behavioral neuroscience.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020 Sep;116:426-435. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.07.009. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020. PMID: 32681940 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimized protocol for conditioned place avoidance learning in juvenile zebrafish.STAR Protoc. 2021 Apr 12;2(2):100465. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100465. eCollection 2021 Jun 18. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33912851 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed chromatic processing at the interface between retina and brain in the larval zebrafish.Curr Biol. 2021 May 10;31(9):1945-1953.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.01.088. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 33636122 Free PMC article.
-
Learning-dependent neuronal activity across the larval zebrafish brain.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;67:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2020.07.006. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32861055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ongoing habenular activity is driven by forebrain networks and modulated by olfactory stimuli.Curr Biol. 2021 Sep 13;31(17):3861-3874.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.08.021. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34416179 Free PMC article.
-
EVIDENCE FOR AUDITORY STIMULUS-SPECIFIC ADAPTATION BUT NOT DEVIANCE DETECTION IN LARVAL ZEBRAFISH BRAINS.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 14:2024.06.14.597058. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.14.597058. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Comp Neurol. 2025 Apr;533(4):e70046. doi: 10.1002/cne.70046. PMID: 38915708 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Al-Imari L., Gerlai R. Sight of conspecifics as reward in associative learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behav. Brain Res. 2008;189:216–219. - PubMed
-
- Aoki R., Tsuboi T., Okamoto H. Y-maze avoidance: an automated and rapid associative learning paradigm in zebrafish. Neurosci. Res. 2015;91:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Braubach O.R., Wood H.-D., Gadbois S., Fine A., Croll R.P. Olfactory conditioning in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behav. Brain Res. 2009;198:190–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

