Prevention of Adult Colitis by Oral Ferric Iron in Juvenile Mice Is Associated with the Inhibition of the Tbet Promoter Hypomethylation and Gene Overexpression
- PMID: 31370166
- PMCID: PMC6723685
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11081758
Prevention of Adult Colitis by Oral Ferric Iron in Juvenile Mice Is Associated with the Inhibition of the Tbet Promoter Hypomethylation and Gene Overexpression
Abstract
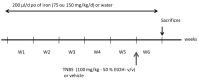
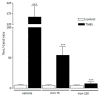
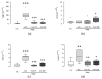
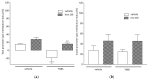
Iron is an essential nutrient needed for physiological functions, particularly during the developmental period of the early childhood of at-risk populations. The purpose of this study was to investigate, in an experimental colitis, the consequences of daily oral iron ingestion in the early period on the inflammatory response, the spleen T helper (Th) profiles and the associated molecular mechanisms. Juvenile mice orally received microencapsulated ferric iron or water for 6 weeks. On adult mice, we induced a sham or experimental trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) moderate colitis during the last week of the experiment before sacrificing the animals 7 days later. The severity of the gut inflammation was assessed by macroscopic damage scores (MDS) and the myeloperoxidase activity (MPO). Th profiles were evaluated by the examination of the splenic gene expression of key transcription factors of the Th differentiation (Tbet, Gata3, Foxp3 and RORγ) and the methylation of their respective promoter. While TNBS-induced colitis was associated with a change of the Th profile (notably an increase in the Tbet/Gata3 ratio in the spleen), the colitis-inhibition induced by ferric iron was associated with a limitation of the splenic Th profiles perturbation. The inhibition of the splenic Tbet gene overexpression was associated with an inhibition of promoter hypomethylation. In summary, mice treated by long-term oral ferric iron in the early period of life exhibited an inhibition of colitis associated with the inhibition of the splenic Tbet promoter hypomethylation and gene overexpression.
Keywords: Tbet; Th profile; ferric iron; intestinal inflammation; promoter methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Juvenile ferric iron prevents microbiota dysbiosis and colitis in adult rodents.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jun 7;18(21):2619-29. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i21.2619. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22690070 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery from TNBS-induced colitis leads to the resistance to recurrent colitis and an increased ratio of FOXP3 to CD3 mRNA.J Dig Dis. 2013 Nov;14(11):587-95. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12084. J Dig Dis. 2013. PMID: 23786412
-
Concurrent infection with Schistosoma mansoni attenuates inflammation induced changes in colonic morphology, cytokine levels, and smooth muscle contractility of trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid induced colitis in rats.Gut. 2004 Jan;53(1):99-107. doi: 10.1136/gut.53.1.99. Gut. 2004. PMID: 14684583 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of recombinant cystatin from Schistosoma japonicum in TNBS-induced experimental colitis of mice.Parasit Vectors. 2016 Jan 4;9:6. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1288-1. Parasit Vectors. 2016. PMID: 26728323 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of recombinant cholera toxin subunit B inhibits IL-12-mediated murine experimental (trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid) colitis.J Immunol. 2001 Mar 1;166(5):3522-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.5.3522. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11207312
Cited by
-
TRIM28 mediates Mettl5 ubiquitination to promotes Th2 polarization.Front Immunol. 2025 May 5;16:1524633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1524633. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40391221 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary energy restriction in neurological diseases: what's new?Eur J Nutr. 2023 Mar;62(2):573-588. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-03036-1. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Eur J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36369305 Review.
-
Iron Supplementation Interferes With Immune Therapy of Murine Mammary Carcinoma by Inhibiting Anti-Tumor T Cell Function.Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 4;10:584477. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.584477. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33344239 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic lactic acid bacteria alleviate pediatric IBD and remodel gut microbiota by modulating macrophage polarization and suppressing epithelial apoptosis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1168924. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1168924. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37396394 Free PMC article.
-
Dust mite antigens endow dendritic cells with the capacity to induce a Th2 response by regulating their methylation profiles.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Dec 18;22(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01986-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39695662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calder P.C., Krauss-Etschmann S., de Jong E.C., Dupont C., Frick J.-S., Frokiaer H., Heinrich J., Garn H., Koletzko S., Lack G., et al. Early nutrition and immunity—Progress and perspectives. Br. J. Nutr. 2006;96:774–790. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

