The Structural Versatility of the BTB Domains of KCTD Proteins and Their Recognition of the GABAB Receptor
- PMID: 31370201
- PMCID: PMC6722564
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9080323
The Structural Versatility of the BTB Domains of KCTD Proteins and Their Recognition of the GABAB Receptor
Abstract
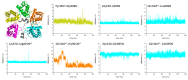
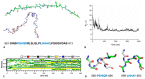
Several recent investigations have demonstrated that members of the KCTD (Potassium Channel Tetramerization Domain) protein family are involved in fundamental processes. However, the paucity of structural data available on these proteins has frequently prevented the definition of their biochemical role(s). Fortunately, this scenario is rapidly changing as, in very recent years, several crystallographic structures have been reported. Although these investigations have provided very important insights into the function of KCTDs, they have also raised some puzzling issues. One is related to the observation that the BTB (broad-complex, tramtrack, and bric-à-brac) domain of these proteins presents a remarkable structural versatility, being able to adopt a variety of oligomeric states. To gain insights into this intriguing aspect, we performed extensive molecular dynamics simulations on several BTB domains of KCTD proteins in different oligomeric states (monomers, dimers, tetramers, and open/close pentamers). These studies indicate that KCTD-BTB domains are stable in the simulation timescales, even in their monomeric forms. Moreover, simulations also show that the dynamic behavior of open pentameric states is strictly related to their functional roles and that different KCTDs may form stable hetero-oligomers. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations also provided a dynamic view of the complex formed by KCTD16 and the GABAB2 receptor, whose structure has been recently reported. Finally, simulations carried out on the isolated fragment of the GABAB2 receptor that binds KCTD16 indicate that it is able to assume the local conformation required for the binding to KCTD.
Keywords: molecular dynamics simulations; oligomerization; protein–protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural complexity in the KCTD family of Cullin3-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligases.Biochem J. 2017 Nov 1;474(22):3747-3761. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170527. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28963344 Free PMC article.
-
KCTD Hetero-oligomers Confer Unique Kinetic Properties on Hippocampal GABAB Receptor-Induced K+ Currents.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 1;37(5):1162-1175. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2181-16.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28003345 Free PMC article.
-
The BTB domains of the potassium channel tetramerization domain proteins prevalently assume pentameric states.FEBS Lett. 2016 Jun;590(11):1663-71. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12203. Epub 2016 May 24. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 27152988
-
BTB domains: A structural view of evolution, multimerization, and protein-protein interactions.Bioessays. 2023 Feb;45(2):e2200179. doi: 10.1002/bies.202200179. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Bioessays. 2023. PMID: 36449605 Review.
-
The emerging role of the KCTD proteins in cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 May 17;19(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00737-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34001146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of the Structural Recognition between KCTD Proteins and Cullin 3.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 4;25(3):1881. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031881. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339159 Free PMC article.
-
KCTD15 deregulation is associated with alterations of the NF-κB signaling in both pathological and physiological model systems.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 14;11(1):18237. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97775-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34521919 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
AlphaFold-Predicted Structures of KCTD Proteins Unravel Previously Undetected Relationships among the Members of the Family.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 10;11(12):1862. doi: 10.3390/biom11121862. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944504 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of the Nrf2/Bach1 Signaling Pathway in Parkinson's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 9;11(9):1780. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091780. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alphafold Predictions Provide Insights into the Structural Features of the Functional Oligomers of All Members of the KCTD Family.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 1;23(21):13346. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113346. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y., Yang Z., Meng M., Zhao Y., Dong N., Yan H., Liu L., Ding M., Peng H.B., Shao F. Cullin Mediates Degradation of RhoA through Evolutionarily Conserved BTB Adaptors to Control Actin Cytoskeleton Structure and Cell Movement. Mol. Cell. 2009;35:841–855. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.09.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

