Roundup®, but Not Roundup-Ready® Corn, Increases Mortality of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 31370250
- PMCID: PMC6789507
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics7030038
Roundup®, but Not Roundup-Ready® Corn, Increases Mortality of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
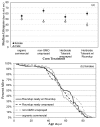
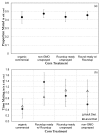
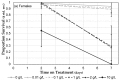
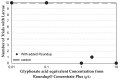
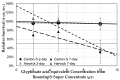
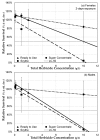
Genetically modified foods have become pervasive in diets of people living in the US. By far the most common genetically modified foods either tolerate herbicide application (HT) or produce endogenous insecticide (Bt). To determine whether these toxicological effects result from genetic modification per se, or from the increase in herbicide or insecticide residues present on the food, we exposed fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster, to food containing HT corn that had been sprayed with the glyphosate-based herbicide Roundup®, HT corn that had not been sprayed with Roundup®, or Roundup® in a variety of known glyphosate concentrations and formulations. While neither lifespan nor reproductive behaviors were affected by HT corn, addition of Roundup® increased mortality with an LC50 of 7.1 g/L for males and 11.4 g/L for females after 2 days of exposure. Given the many genetic tools available, Drosophila are an excellent model system for future studies about genetic and biochemical mechanisms of glyphosate toxicity.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; LC50; Roundup®; genetically modified food; glyphosate; herbicide tolerant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Toxicological Effects of Roundup® on Drosophila melanogaster Reproduction.Toxics. 2021 Jul 7;9(7):161. doi: 10.3390/toxics9070161. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34357904 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Behavior of Drosophila melanogaster Fed with Genetically-Modified Corn or Roundup®.J Xenobiot. 2021 Dec 17;11(4):215-227. doi: 10.3390/jox11040014. J Xenobiot. 2021. PMID: 34940514 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of broiler performance when fed diets containing grain from roundup ready (NK603), yieldgard x roundup ready (MON810 x NK603), non-transgenic control, or commercial corn.Poult Sci. 2003 Mar;82(3):443-53. doi: 10.1093/ps/82.3.443. Poult Sci. 2003. PMID: 12705406
-
Safety evaluation and risk assessment of the herbicide Roundup and its active ingredient, glyphosate, for humans.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2000 Apr;31(2 Pt 1):117-65. doi: 10.1006/rtph.1999.1371. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10854122 Review.
-
Glyphosate, Roundup and the Failures of Regulatory Assessment.Toxics. 2022 Jun 13;10(6):321. doi: 10.3390/toxics10060321. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35736929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicological Effects of Roundup® on Drosophila melanogaster Reproduction.Toxics. 2021 Jul 7;9(7):161. doi: 10.3390/toxics9070161. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34357904 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Behavior of Drosophila melanogaster Fed with Genetically-Modified Corn or Roundup®.J Xenobiot. 2021 Dec 17;11(4):215-227. doi: 10.3390/jox11040014. J Xenobiot. 2021. PMID: 34940514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- USDA ERS, United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service Adoption of Genetically Modified Crops in the US. [(accessed on 20 April 2018)];2017 Available online: https://www ers.usda.gov/data-products/adoption-of-genetically-engineere...
-
- Fernandez-Cornejo J., Wechsler S.J., Milkove D.L. The Adoption of Genetically Engineered Alfalfa, Canola and Sugarbeets in the United States. United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; Washington, DC, USA: 2016.
-
- ISAAA . ISAAA Brief No. 52: Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2016. ISAAA; Ithaca, NY, USA: 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

