New Insights about the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Primary Bone Tumors and Their Microenvironment: A Promising Target to Develop Therapeutic Strategies?
- PMID: 31370265
- PMCID: PMC6696068
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20153751
New Insights about the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Primary Bone Tumors and Their Microenvironment: A Promising Target to Develop Therapeutic Strategies?
Abstract
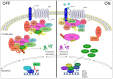
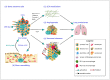
Osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma are the most common malignant primary bone tumors mainly occurring in children, adolescents and young adults. Current standard therapy includes multidrug chemotherapy and/or radiation specifically for Ewing sarcoma, associated with tumor resection. However, patient survival has not evolved for the past decade and remains closely related to the response of tumor cells to chemotherapy, reaching around 75% at 5 years for patients with localized forms of osteosarcoma or Ewing sarcoma but less than 30% in metastatic diseases and patients resistant to initial chemotherapy. Despite Ewing sarcoma being characterized by specific EWSR1-ETS gene fusions resulting in oncogenic transcription factors, currently, no targeted therapy could be implemented. It seems even more difficult to develop a targeted therapeutic strategy in osteosarcoma which is characterized by high complexity and heterogeneity in genomic alterations. Nevertheless, the common point between these different bone tumors is their ability to deregulate bone homeostasis and remodeling and divert them to their benefit. Therefore, targeting different actors of the bone tumor microenvironment has been hypothesized to develop new therapeutic strategies. In this context, it is well known that the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays a key role in cancer development, including osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma as well as in bone remodeling. Moreover, recent studies highlight the implication of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in angiogenesis and immuno-surveillance, two key mechanisms involved in metastatic dissemination. This review focuses on the role played by this signaling pathway in the development of primary bone tumors and the modulation of their specific microenvironment.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin; bone sarcoma; bone tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ladenstein R., Pötschger U., Le Deley M.C., Whelan J., Paulussen M., Oberlin O., van den Berg H., Dirksen U., Hjorth L., Michon J., et al. Primary disseminated multifocal Ewing sarcoma: Results of the Euro-EWING 99 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:3284–3291. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.9864. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

