Precise Long-Range Microcircuit-to-Microcircuit Communication Connects the Frontal and Sensory Cortices in the Mammalian Brain
- PMID: 31371111
- PMCID: PMC6813886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.06.028
Precise Long-Range Microcircuit-to-Microcircuit Communication Connects the Frontal and Sensory Cortices in the Mammalian Brain
Abstract
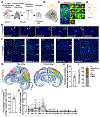
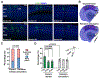
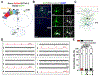
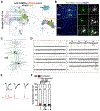
The frontal area of the cerebral cortex provides long-range inputs to sensory areas to modulate neuronal activity and information processing. These long-range circuits are crucial for accurate sensory perception and complex behavioral control; however, little is known about their precise circuit organization. Here we specifically identified the presynaptic input neurons to individual excitatory neuron clones as a unit that constitutes functional microcircuits in the mouse sensory cortex. Interestingly, the long-range input neurons in the frontal but not contralateral sensory area are spatially organized into discrete vertical clusters and preferentially form synapses with each other over nearby non-input neurons. Moreover, the assembly of distant presynaptic microcircuits in the frontal area depends on the selective synaptic communication of excitatory neuron clones in the sensory area that provide inputs to the frontal area. These findings suggest that highly precise long-range reciprocal microcircuit-to-microcircuit communication mediates frontal-sensory area interactions in the mammalian cortex.
Keywords: columnar microcircuit; cortical circuit; excitatory neuron clone; in utero retroviral labeling; long-range circuit; quadruple whole-cell recording; rabies virus tracing; top-down modulation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Aronoff R, Matyas F, Mateo C, Ciron C, Schneider B, and Petersen CC (2010). Long-range connectivity of mouse primary somatosensory barrel cortex. The European journal of neuroscience 31, 2221–2233. - PubMed
-
- Bloom JS, and Hynd GW (2005). The role of the corpus callosum in interhemispheric transfer of information: excitation or inhibition? Neuropsychology review 15, 59–71. - PubMed
-
- Buschman TJ, and Miller EK (2007). Top-down versus bottom-up control of attention in the prefrontal and posterior parietal cortices. Science 315, 1860–1862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

