Highly diversified shrew hepatitis B viruses corroborate ancient origins and divergent infection patterns of mammalian hepadnaviruses
- PMID: 31371507
- PMCID: PMC6708359
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1908072116
Highly diversified shrew hepatitis B viruses corroborate ancient origins and divergent infection patterns of mammalian hepadnaviruses
Abstract
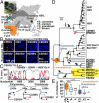
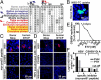
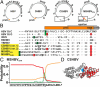
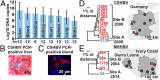
Shrews, insectivorous small mammals, pertain to an ancient mammalian order. We screened 693 European and African shrews for hepatitis B virus (HBV) homologs to elucidate the enigmatic genealogy of HBV. Shrews host HBVs at low prevalence (2.5%) across a broad geographic and host range. The phylogenetically divergent shrew HBVs comprise separate species termed crowned shrew HBV (CSHBV) and musk shrew HBV (MSHBV), each containing distinct genotypes. Recombination events across host orders, evolutionary reconstructions, and antigenic divergence of shrew HBVs corroborated ancient origins of mammalian HBVs dating back about 80 million years. Resurrected CSHBV replicated in human hepatoma cells, but human- and tupaia-derived primary hepatocytes were resistant to hepatitis D viruses pseudotyped with CSHBV surface proteins. Functional characterization of the shrew sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (Ntcp), CSHBV/MSHBV surface peptide binding patterns, and infection experiments revealed lack of Ntcp-mediated entry of shrew HBV. Contrastingly, HBV entry was enabled by the shrew Ntcp. Shrew HBVs universally showed mutations in their genomic preCore domains impeding hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) production and resembling those observed in HBeAg-negative human HBV. Deep sequencing and in situ hybridization suggest that HBeAg-negative shrew HBVs cause intense hepatotropic monoinfections and low within-host genomic heterogeneity. Geographical clustering and low MSHBV/CSHBV-specific seroprevalence suggest focal transmission and high virulence of shrew HBVs. HBeAg negativity is thus an ancient HBV infection pattern, whereas Ntcp usage for entry is not evolutionarily conserved. Shrew infection models relying on CSHBV/MSHBV revertants and human HBV will allow comparative assessments of HBeAg-mediated HBV pathogenesis, entry, and species barriers.
Keywords: E antigen; hepatitis B virus; shrew; viral evolution; zoonosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

