The roles of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in cryopreservation
- PMID: 31371631
- PMCID: PMC6712439
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20191601
The roles of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in cryopreservation
Abstract
Cryopreservation has facilitated advancement of biological research by allowing the storage of cells over prolonged periods of time. While cryopreservation at extremely low temperatures would render cells metabolically inactive, cells suffer insults during the freezing and thawing process. Among such insults, the generation of supra-physiological levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) could impair cellular functions and survival. Antioxidants are potential additives that were reported to partially or completely reverse freeze-thaw stress-associated impairments. This review aims to discuss the potential sources of cryopreservation-induced ROS and the effectiveness of antioxidant administration when used individually or in combination.
Keywords: Cryopreservation; antioxidant; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
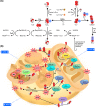
 ); Cu1+/Fe2+ (
); Cu1+/Fe2+ ( ); Source of ROS (
); Source of ROS ( ); Enzyme (
); Enzyme ( ); O2•− (
); O2•− ( ); O2 (
); O2 ( ); H2O (
); H2O ( ); H2O2 (
); H2O2 ( ); •OH (
); •OH ( ); ONOO− (
); ONOO− ( ); NO• (
); NO• ( ); NO2− (
); NO2− ( ); H+ (
); H+ ( ); Detected during cryopreservation (
); Detected during cryopreservation ( ); Implicated during cryopreservation (
); Implicated during cryopreservation ( ).
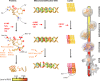
).
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

