Early Phase II Comprehensive Cardiac Rehabilitation after Acute Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 31371904
- PMCID: PMC6656979
- DOI: 10.6515/ACS.201907_35(4).20190330A
Early Phase II Comprehensive Cardiac Rehabilitation after Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Cardiac rehabilitation is beneficial for patients after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). However, most institutes perform outpatient training phase (phase II) of post-MI cardiac rehabilitation after 2-4 weeks. To evaluate the possibility of performing cardiac rehabilitation with an earlier schedule after STEMI.
Methods: We conducted a series of early phase II cardiac rehabilitation starting from 5-7 days after STEMI, including the training group (n = 28) and the control group (n = 42).
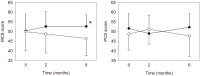
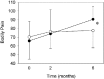
Results: The results showed an improved mental component summary of the SF-36 questionnaire after 6 months in the training group. No adverse event was noticed during this early phase II training.
Conclusions: Cardiac rehabilitation after STEMI might be started earlier than previously thought for clinical use or further research.
Keywords: Acute myocardial infarction; Cardiac rehabilitation; Exercise training; Mental health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation on the Mid-Term Outcomes of Patients After Acute Myocardial Infarction Treated With Current Acute-Phase Management and Optimal Medical Therapy.Heart Lung Circ. 2021 Sep;30(9):1320-1328. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2021.03.268. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Heart Lung Circ. 2021. PMID: 33867276
-
Early- and late-term clinical outcome and their predictors in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Nov 15;169(4):254-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.08.132. Epub 2013 Sep 8. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24071385
-
Cardiac rehabilitation in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: can its failure be predicted?Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 Jul;11(7):177-184. doi: 10.1177/1753944717706845. Epub 2017 May 29. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28553755 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of different initiation time of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling and cardiopulmonary rehabilitation in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction.Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(3):268-76. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1036174. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Disabil Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 25885667 Review.
-
Cardiac rehabilitation after STEMI.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2018 Aug;66(4):464-470. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4725.18.04674-1. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2018. PMID: 29589673 Review.
Cited by
-
Considering ISCHEMIA in the Context of FAME and FAME 2: A Call for the Universal Adoption of Invasive Ischemia-Guided Coronary Intervention Approach in Chronic Coronary Syndrome.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2020 Mar;36(2):93-96. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202003_36(2).20200303A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2020. PMID: 32201458 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors and COVID-19: Potential Therapeutics Rather Than Perpetrators.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2020 May;36(3):179-182. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202005_36(3).20200430A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2020. PMID: 32425432 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cerebral Oxygenation during Exercise in Patients with Cardiopulmonary Diseases: A Prospective Observational Study.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2020 Nov;36(6):667-674. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202011_36(6).20200519C. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2020. PMID: 33235424 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of early home-based exercise for cardiac rehabilitation on the prognosis of patients with acute myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Jul 15;13(7):7839-7847. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34377261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taylor RS, Brown A, Ebrahim S, et al. Exercise-based rehabilitation for patients with coronary heart disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Med. 2004;116:682–692. - PubMed
-
- Lawler PR, Filion KB, Eisenberg MJ. Efficacy of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation post-myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am Heart J. 2011;162:571–584. - PubMed
-
- Izawa K, Hirano Y, Yamada S, et al. Improvement in physiological outcomes and health-related quality of life following cardiac rehabilitation in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ J. 2004;68:315–320. - PubMed
-
- Yu CM, Lau CP, Chau J, et al. A short course of cardiac rehabilitation program is highly cost effective in improving long-term quality of life in patients with recent myocardial infarction or percutaneous coronary intervention. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85:1915–1922. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
