The frequency of non-pathologically thin corneas in young healthy adults
- PMID: 31371912
- PMCID: PMC6628863
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S188935
The frequency of non-pathologically thin corneas in young healthy adults
Abstract
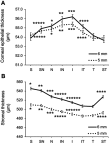
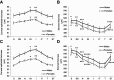
Purpose: Measurement of normal corneal thickness and corneal epithelial thickness is important in keratorefractive surgery, glaucoma, following extended contact lens wear, and in patients with corneal disease. Clinically, a central corneal thickness less than 500 µm is considered to be moderately-to-extremely thin. The purpose of this study was to compare biological differences in patients with clinically thin compared to normal corneal thickness values in healthy young adults using Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. Patients and methods: In total, 168 eyes from 84 patients aged 19-38 years were scanned using an Avanti optical coherence tomographer. To eliminate circadian effects on corneal thickness, all patients were scanned within a 4-hour window. Corneal thickness was measured across the central 6 mm of the cornea. Total central corneal thickness, corneal epithelial thickness, and corneal stromal thickness were compared between males and females and tested for correlations with age, use of systemic hormones, degree of myopia, and corneal curvature. Results: The average central corneal thickness for males and females was 540.5±32.0 μm and 525.2±33.0 μm, respectively (P=0.020). Thirty-eight eyes had corneal thickness measurements below 500 µm; 12% (6 eyes) from males and 28% (16 eyes) from females (P=0.008). All women with corneas below 500 μm were bilaterally thin. This finding differed for men. Corneal thinning was not associated with age, use of systemic hormones, or degree of myopia. Females had steeper keratometry (K) readings (P=0.01 for flat K, P=0.002 for steep K) than males. No differences in layer offset values between normal thickness corneas and thin corneas were evident, suggesting that the reduced thickness was not pathological. Conclusion: The results of this study indicate that a subpopulation of healthy young adults have non-pathologically thin corneas, well below 500 μm; and that these thinner corneas are more frequent in females. This underscores the importance of accurate corneal thickness measurements prior to keratorefractive surgery and when evaluating intraocular pressure in glaucoma.
Keywords: OCT; cornea; epithelial; stroma; thickness.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Danielle M Robertson reports grants from Alcon Laboratories for colleting data as part of a larger study. The data presented does not relate to any of Alcon's products. Grants from Alcon Laboratories were for an investigator-designed research study. Alcon had no input in the study design or analysis/interpretation of any of the data. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effects of long-term contact lens wear on corneal thickness, curvature, and surface regularity.Ophthalmology. 2000 Jan;107(1):105-11. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(99)00027-5. Ophthalmology. 2000. PMID: 10647727
-
Contact lens-assisted collagen cross-linking (CACXL): A new technique for cross-linking thin corneas.J Refract Surg. 2014 Jun;30(6):366-72. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20140523-01. J Refract Surg. 2014. PMID: 24972403
-
Central corneal thickness, tonometry, and ocular dimensions in glaucoma and ocular hypertension.J Glaucoma. 2001 Jun;10(3):206-10. doi: 10.1097/00061198-200106000-00011. J Glaucoma. 2001. PMID: 11442184
-
Repeatability of Cornea and Sublayer Thickness Measurements Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Corneas of Anomalous Refractive Status.J Refract Surg. 2019 Sep 1;35(9):600-605. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20190806-03. J Refract Surg. 2019. PMID: 31498418
-
Corneal epithelial thickness mapping using Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography for detection of form fruste keratoconus.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015 Apr;41(4):812-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2014.06.043. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015. PMID: 25840306
Cited by
-
Thin but Nonkeratoconic Cornea: A Case Report.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec;36(6):565-567. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2022.0053. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36220640 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Validation of a Novel Low-Cost Glaucoma Risk Calculator for Community-Based Screening in High-Risk Populations.Clin Ophthalmol. 2025 Feb 3;19:357-369. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S500509. eCollection 2025. Clin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39926312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavanagh HD, Ladage PM, Li SL, et al. Effects of daily and overnight wear of a novel hyper oxygen-transmissible soft contact lens on bacterial binding and corneal epithelium. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:1957–1969. - PubMed
-
- Ladage PM, Yamamoto K, Ren DH, et al. Effects of rigid and soft contact lens daily wear on corneal epithelium, tear lactate dehydrogenase, and bacterial binding to exfoliated epithelial cells. Ophthalmology. 2001;108:1279–1288. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg ME, Tervo TM, Immonen IJ, Muller LJ, Gronhagen-Riska C, Vesaluoma MH. Corneal structure and sensitivity in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41(10):2915–2921. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

