Different durations of cognitive stimulation therapy for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31371930
- PMCID: PMC6635834
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S210062
Different durations of cognitive stimulation therapy for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to evaluate the efficacy of cognitive stimulation therapy (CST) of different durations for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
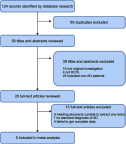
Methods: A comprehensive search was carried out in three databases. The primary outcome was Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score. We conducted a meta-analysis with Review Manager, version 5.3 and assessed the methodological quality of the included studies using the Cochrane Collaboration Recommendations assessment tool.
Results: Treatment effects from the meta-analysis showed that CST plus acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs) was better than the control assessed by MMSE. In addition, the meta-analysis indicated that long-term CST was better than short-term or maintenance CST.
Conclusion: Our study confirmed that the combination of CST and drug treatment for AD is effective in AD, regardless of whether short-term CST, maintenance CST, or long-term CST is used. The long-term CST appears to be more effective.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cognitive stimulation therapy; cognitive symptom; meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


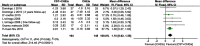
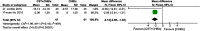

References
-
- Ltd TT. Pharmaceuticals innovation in neurodegeneration. 2016; Available from: http://taurx.com/taurx-phase-3-trial-trx-237-007-in-behavioural-variant-.... Accessed 22July, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

