Antiangiogenic properties of nanoparticles: a systematic review
- PMID: 31371952
- PMCID: PMC6630093
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S199974
Antiangiogenic properties of nanoparticles: a systematic review
Abstract
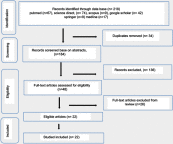
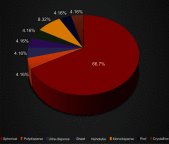
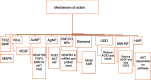
Nanoparticles appear to be one of the most promising agents that offer efficacy in angiogenesis-related disease therapy. The objective of this research is to systematically review studies that have probed into the effect of nanoparticles on angiogenesis. Selected inclusion criteria were used to extract articles, references that were cited in the initial search were sought to identify more potential articles, and articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria and duplicates were discarded. The spherical shape was shown to be the most common shape employed to investigate the role of nanoparticles in angiogenesis therapy. The size of nanoparticles appears to play a crucial role for efficacy on angiogenesis, in which 20 nm emerged as the preferred size. Gold nanoparticles exhibit the most promise as an antiangiogenesis agent, and the toxicity was adjustable based on the dosages applied.
Keywords: angiogenesis; antiangiogenesis; nanoparticles; shape; size; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

